Gout Treatment
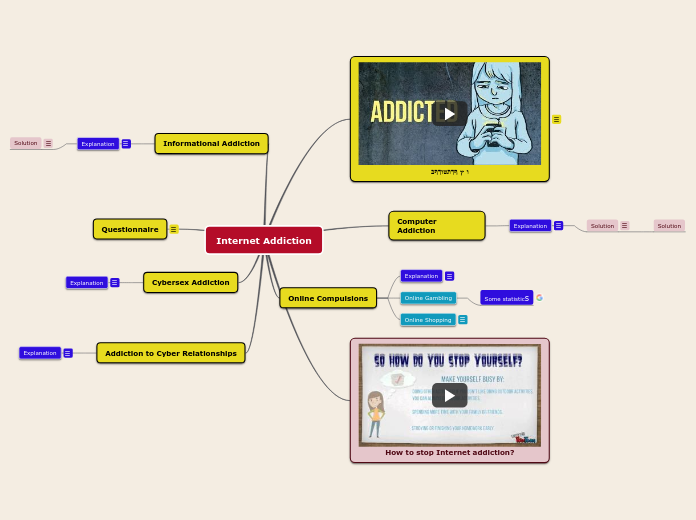
dz produced by the formation of uric acid crystals (tophi) in joints (b/c there's low fluid there), especially in the big toe
the crystals provoke an immune response
granulocytes respond and their high metabolic activity produces lactic acid, reducing pH and causing more uric acid to precipitate
CHRONIC
Increase uric acid excretion
Sulfinpyrazole
MOA same as probenecid
hypersensitivity not common
GI side effects
other uses:
antithrombic (like aspirin)
Probenecid (high doses)
@ high doses, inhibits secretion + reabsorbtion
incr. excretion decr. plasma urate(what we want in a gout treatment -- whatever's in there just passes right thru)
@ low doses, inhibits secretion not reabsorbtion
decr. excretion incr. plasma uratedrug must be in filtrate to act on transporters on the apical surface
complications
it antagonizes diuretics
aspirin prevents its action
may use tylenol or naproxen insteadpredisposes to kidney stone
b/c it decreases pHGI disurbances
other uses
uncomplicated gonoccocal infxn
only takes one shotMOA: inhibits penicillin excretion via nonspecific OAT 1 & 3Reduce uric acid synthesis
Allopurinol
MOA: inhibits xanthine oxidase
80% bioavailabilityit is a xanthine isomerContraindications
acute gouty attack
may worsen an acute gouty attack if used as 1st tx
ACUTE
Reduce inflammation
Colchicine
MOA: inhibits activities of leukocytes (esp. granulocytes)
AE:
severe n/v, limits effectiveness