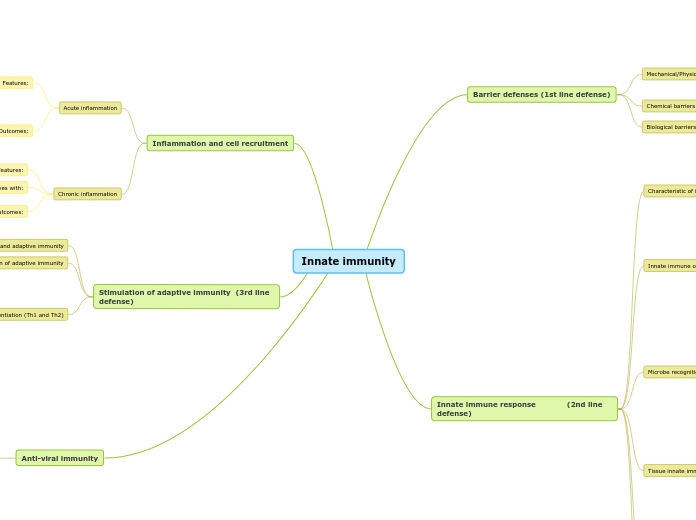
Innate immunity
Anti-viral immunity
type I IFNs (α/ß) or IFN-I
detect RNA and DNA viruses with two endosomal sensors, TLR7
and TLR9
primary source of IFN-I for antiviral responses
Stimulation of adaptive immunity (3rd line defense)
T cell activation and differentiation (Th1 and Th2)
Th2
-antibody-mediated immunity
-extracellular parasites
-asthma, allergy
Th1
-cell-mediated immunity and inflammation
-intracellular pathogens
-autoimmunity
-inflammation
Activation of adaptive immunity
Interplay between innate and adaptive immunity
Inflammation and cell recruitment
Chronic inflammation
• Scarring
• Amyloidosis
• Neoplasia
Mechanism involves with:
Pro-inflammatory(IFN-γ)and anti-inflammatory (IL-4andIL-13)
Prolonged exposure to toxic pathogens
Acute inflammation
Outcomes:
1. Local hemodynamic changes (vasoconstriction → vasodilation)
2. Increase in vascular permeability
3. Extravasation of leukocytes
4. Phagocytosis
5. Outcome of inflammatory response
Features:
5 cardinal signs: redness, increased heat, swelling, pain, loss of function
Involves the innate immune system
Innate immune response (2nd line defense)
Humoral substances of innate immunity
Cytokines, mediators, complement system
Peripheral blood immune cells
Monocytes
Basophils
Eosinophils
is involved in host protection against parasite infection and
immunopathology in hypersensitivity disease
Dendritic cells
are professional antigen-presenting cells
Neutrophils
are important effector cells in the innate arm of the
immune system.
NK cells
-recognize MHC I
-Produce high levels of cytokines
Tissue innate immune cells
Macrophages
secretes inflammatory cytokines that support immune responses.
Intraepithelial lymphocyte (IELs)
an effective first line of defense
are lymphocytes found in the epithelial layer of mammalian mucosal linings
Microbe recognition by innate immune cell PRRs
Major type of PRRs
C-type lectin receptors (CLRs)
RIG-like receptors (RLRs)
NOD-like receptors (NLRs)
Toll-like receptors (TLRs)
PRRs can be found on the innate immune cells
PRRs are able to recognize molecules associated with pathogens i.e. PAMPs and DAMPs
Innate immune cell activation by PAMPs and DAMPs
DAMPs
Endogenous stimuli
Derived from host cells such as tumor cells, dead or dying cells, products released from cells, tissue damage, etc
PAMPs
Exogenous stimuli
Derived from components of microorganisms (pathogens)
Characteristic of innate immunity
No memory
Non-specific responses
Rapid/quick response
Barrier defenses (1st line defense)
Biological barriers
ex. normal flora
is the term used to describe various bacteria and fungi that are permanent residents of certain body sites
Chemical barriers
ex. low stomach pH, lysozyme
Mechanical/Physical barriers
ex. skin
tightly joined
preventing
microbes from reaching tissues