av Adam Bright 11 år siden
513
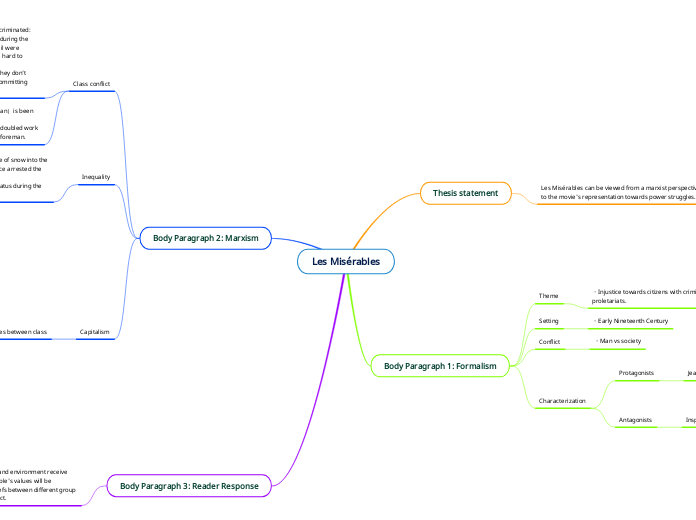
8th Grade history- Social Science Curriculum
The curriculum for an 8th-grade social science class covers various important historical and economic concepts. It discusses the advantages of a common market among states as envisioned in the U.