av Fatma Bazilah 5 år siden
202
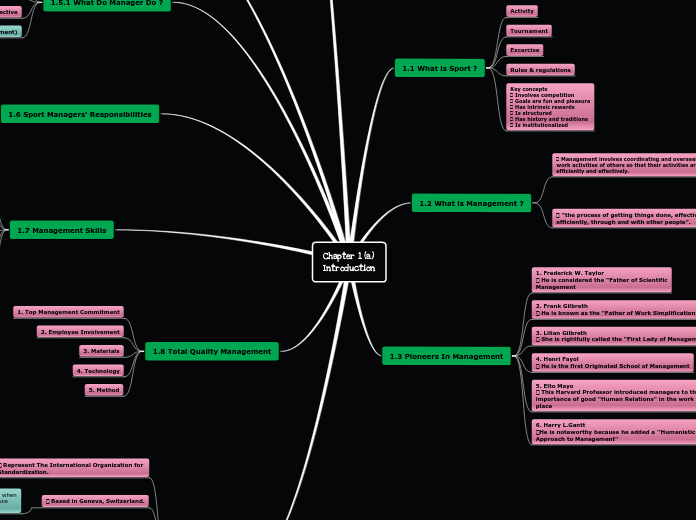
Chapter 1 (a) & 1 (b) Introduction
The distinction between managers and operative employees is fundamental, with managers directing activities and operatives working directly on tasks. A manager is defined as an individual responsible for overseeing more than one person within an organization.