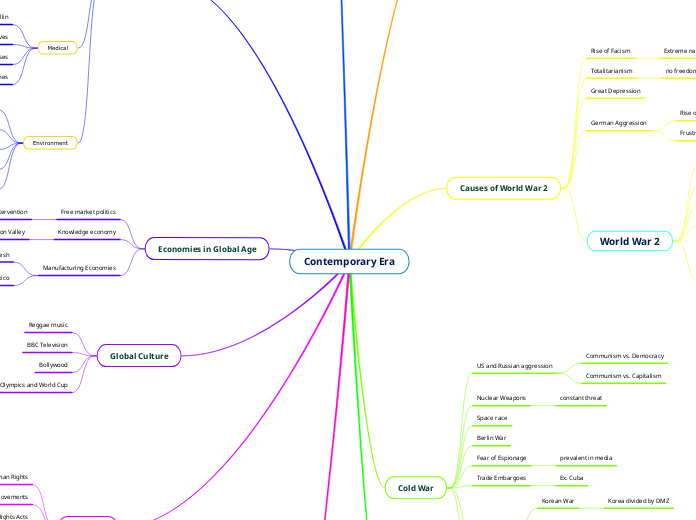
Contemporary Era
Causes of World War 1
World War 1
US superpower
League of nations failure
Used in World War 2 to provide raw materials and manpower
Western States in Asia and Africa
National Independence Movement in India
Japanese in Korea and invades China
Treaty of Versailles forcing Germany to pay billions
Russia 5 year plan
Food shortage
Made USSR more stable
developing industry
Roosevelt's New Deal
Work relief for unemployed
Bank failures
Collapse of world trade
Stock Market Crash
New weapons; machine guns, grenades
Total war
New nation-states
Nationalism
Imperialism
Militarism
Alliances between nations
Assasination of Archduke
Reforms
Anti-apartheid movement
Anti-IMF activism
Greenpeace movements
US Civil Rights Acts
Feminist Movements
UN Declaration of Human Rights
Global Culture
Olympics and World Cup
Bollywood
BBC Television
Reggae music
Economies in Global Age
Manufacturing Economies
Mexico
NAFTA
Economic Institutions and Trade Agreements
WHO
ASEAN
Ex. Bangladesh
Cheaper production
Knowledge economy
Ex. Silicon Valley
Free market politics
no government intervention
Advances
Environment
Greenhouse gases
Consumption of fresh water
Decline in air quality
Deforestation
Desertification
Medical
Vaccines
Emerging epidemic diseases
Contraceptives
Penicillin
Green Revolution
Damage to environment
More food production
New fertilizers and pesticides
Energy
Nuclear Energy
Natural Gas
Petroleum
Transportation
Shipping containers
Air travel
Communication
Internet
TV's and Phones
Radios
New States
Pakistan
Tensions over Kashmir
Chaotic partition
Famine took 2 million lives
Cultural revolution
Wanted independence from France
Israel
Arab and Jewish sections
Israel and Palestine conflict
Creation of Israel due to Zionist movement
Decolonization
Intensification of conflict
Shining Path
Terrorism in Peru
Al-Qaeda
Osama Bin Laden
India
Muslim League
Led to creation of Pakistan
Indian National Congress
Non violent protests
Inspired Nelson Mandela
Inspired Civil Rights movement
Partition of India
Land reasource and redistribution
Kerala
White revolution in Iran
End of Cold War
USSR and US economy broken
End of Soviet Union
Berlin War taken down
Improvements in relationship between US and USSR
Cold War
Non-aligned movement
Greater acceptance of newly created nations
Self-determinations, and sovereignty
Countries in Asia and Africa
Proxy Wars
Angolan Civil War
Cease fire
3 culturally distinct groups backed by South Africa, US, and USSR
Korean War
Korea divided by DMZ
Trade Embargoes
Ex. Cuba
Fear of Espionage
prevalent in media
Berlin War
Space race
Nuclear Weapons
constant threat
US and Russian aggression
Communism vs. Capitalism
Communism vs. Democracy
Causes of World War 2
World War 2
Genocides
Rwanda
Armenia
Cambodia
Ukraine
Atomic bomb; Hiroshima and Nagasaki
Collapse of Europe's Economy
Creation of NATO, EU, and UN
NATO trying to stop spread of communism
60 million casualties
German Aggression
Frustration with Treaty of Versailles
Rise of Nazi Party
Holocaust
Great Depression
Totalitarianism
no freedom
Rise of Facism
Extreme nationalism; Italy
Collapse of Empires
Qing Empire
The Republic of China
Great Leap Forward
20 million died from famine
Collectivization of agriculture
Industrialization
Death of opposers
Heavy Industry
5 year plans
Redistribution of land to peasants
Russian Empire
The Soviet Union
Limited free speech
Communism
Ottoman Empire
Turkey