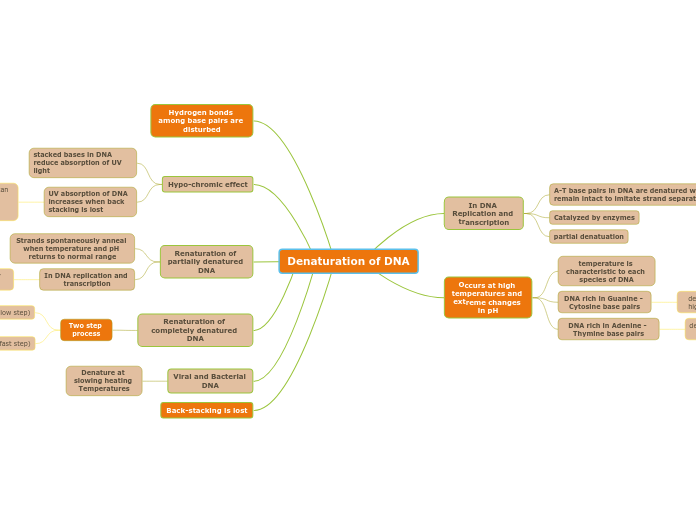
Denaturation of DNA
Type in the name or subject of your brainstorming
Back-stacking is lost
Viral and Bacterial DNA
Denature at slowing heating Temperatures
Occurs at high temperatures and extreme changes in pH
DNA rich in Adenine - Thymine base pairs
denatures at lower temperatures
DNA rich in Guanine - Cytosine base pairs
denatures at very high temperatures
temperature is characteristic to each species of DNA
In DNA Replication and transcription
partial denatuation
Catalyzed by enzymes
A-T base pairs in DNA are denatured while G-T remain intact to imitate strand separation
called bubbles
Renaturation of completely denatured DNA
Two step process
2nd (fast step)
spontaneous annealing of unpaired bases
1st step (Slow step)
By random collisions strands find each other
Renaturation of partially denatured DNA
In DNA replication and transcription
catalyzed by enzymes
Strands spontaneously anneal when temperature and pH returns to normal range
Hypo-chromic effect
UV absorption of DNA increases when back stacking is lost
denatured DNA can be detected by monitoring UV absoprtion
stacked bases in DNA reduce absorption of UV light
Hydrogen bonds among base pairs are disturbed