av William Rumble 9 måneder siden
74
Philosophy and Ethics
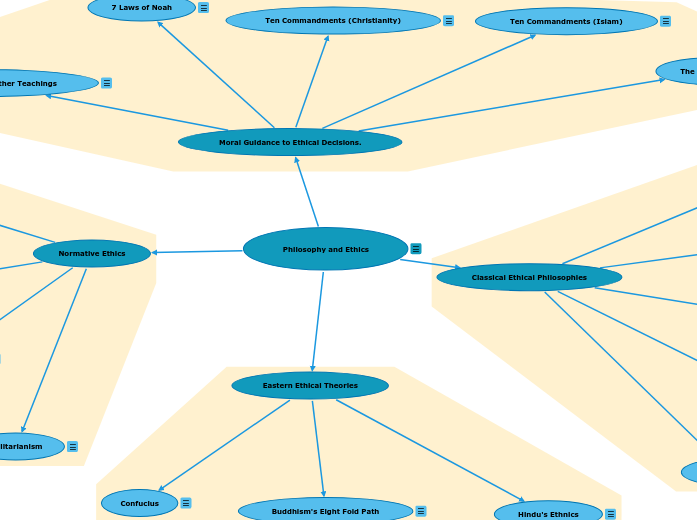
Philosophy is the study of fundamental questions about existence, knowledge, and values through critical analysis and reflection. Within ethics, various theories offer different approaches.
av William Rumble 9 måneder siden
74

Mer som dette
Philosophy is the study of questions about existence, knowledge, values, reason, mind etc. Often through critival analysis, debate, and reflection.
Treat others how you wish to be treated.
Cynicism says that the way to achieve a good life is not through material things but by living a simple, virtuous life in harmony with nature.
Epicureanism is similar to cynicism but less extreme, they advocate for simple living, moderation, and rational thought.
Stoicism, which has gained popularity recently with young men, is the belief that events in life are predetermined and the only thing we control is how we react to them.
Plato believed ethics could be achieved through rational thought and reasoning. He argued that getting philosophical wisdom allows reason to rule and create an ethical person.
Unlike Plato, Aristotle viewed ethics on the individual level. He believed that ethics looks different for everyone and should be achieved by looking at your surroundings and reflecting and adjusting.
The Eight Fold Path goes like this:
Hindu ethics is derived from your Dharma (duty), Karma (cause and effect), and Moksha (liberation). Key values include non-violence, truthfulness, non-stealing, self discipline, and non-possessiveness.
Confucius believed that an ethical existence could exist through the cultivation of virtuous individuals as the practice of ethical relationships. Those relationships are these:
His views on ethics were very hierarchical.
Deontology judges if a choice is ethical or not by the intention behind it and argues that actions are right if they adhere to one's moral duties and obligations.
Utilitarianism advocates to do things that give you happiness instead of ones that make you sad. Also it judges the ethics of one's actions by the outcome, so the ends justify the means.
Virtue ethics looks to do virtuous traits like honesty, courage, and compassion to guide ethical decisions. Virtue ethics focuses on character rather than rules or consequences.
Contractarianism theories say that ethical principles stem from a social contract where people agree on rules for mutual benefit. It focuses on rational self interest within the agreed upon framework.