av Hansa Soomro 6 år siden
277
SUMMARY SHEETS
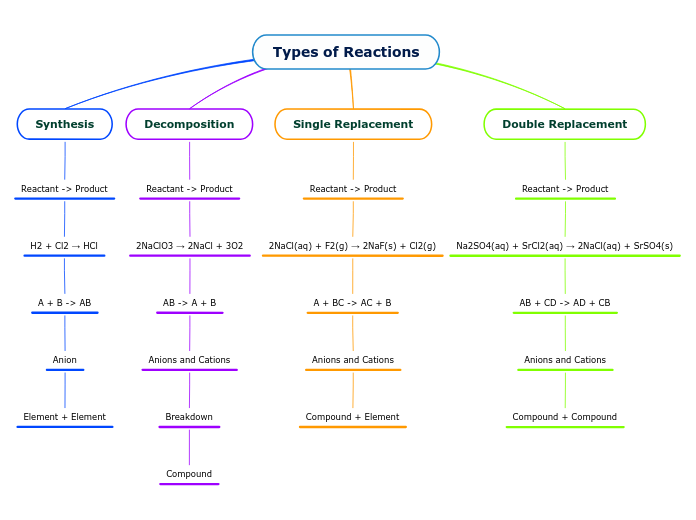
Understanding chemical reactions requires a grasp of various fundamental concepts. Atoms are represented by element symbols, and the number of atoms is indicated by subscripts. Coefficients in chemical equations help balance the reactions by multiplying the subscripts of the elements involved.