por Danial Fadzil 5 anos atrás
200
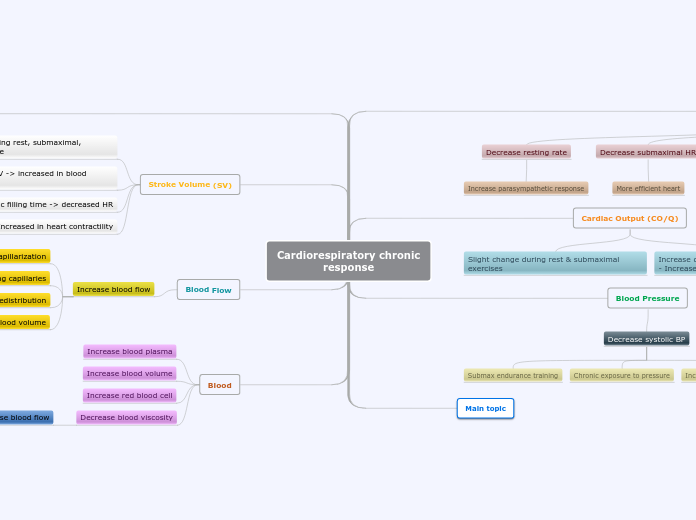
Cardiorespiratory chronic response
Regular cardiorespiratory exercise induces several chronic adaptations in the cardiovascular system. Blood flow enhancements occur through increased capillarization and the opening of existing capillaries, leading to more efficient blood redistribution and increased blood volume.