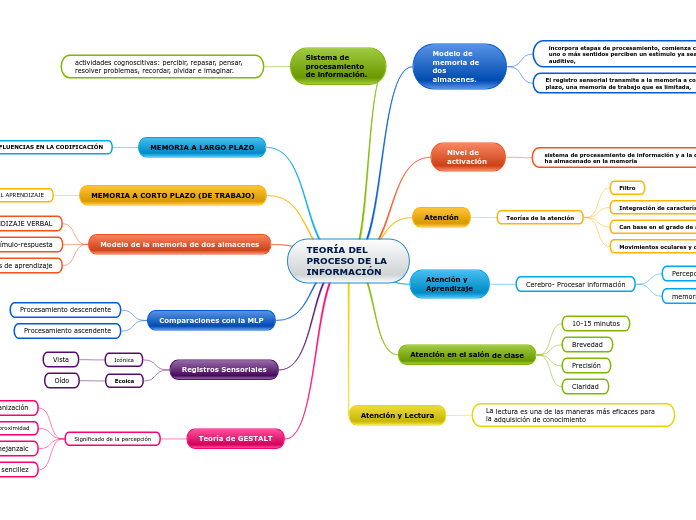
Regulación emocional
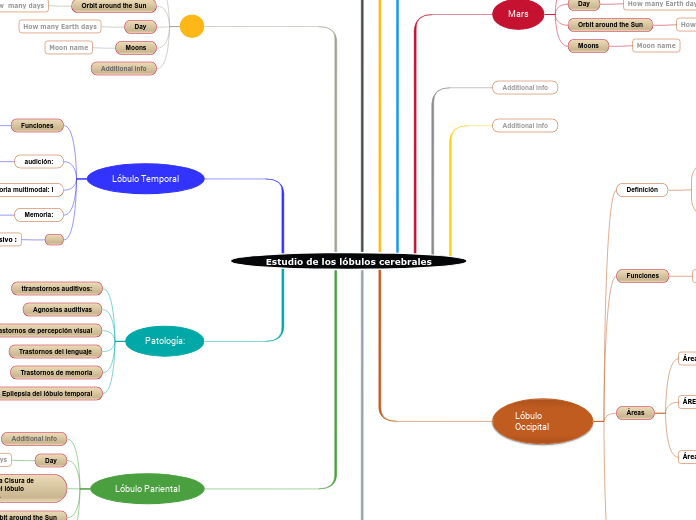
Estudio de los lóbulos cerebrales
The Solar System is the gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it, either directly or indirectly. Of the objects that orbit the Sun directly, the largest are the eight planets, with the remainder being smaller objects, the dwarf planets, and small Solar System bodies.
Lóbulo Pariental
Saturn is known most for its rings.
Galileo Galilei first thought it was an object with three parts: a planet and two large moons on either side.
Not knowing he was seeing a planet with rings, the stumped astronomer entered a small drawing — a symbol with one large circle and two smaller ones — in his notebook.
The rings are made of ice and rock and scientists are not yet sure how they formed. The gaseous planet is mostly hydrogen and helium.
How long does it take for Saturn to go around the sun?
Todo el territorio situado por debajo de la Cisura de Silvio y su prolongación, limitando con el lóbulo occipital y parietal por su zona posterior.
A planet's day is the time it takes the planet to rotate or spin once on its axis.
Write down Saturn's day measured in Earth days.
Patología:
Uranus is an oddball. It has clouds made of hydrogen sulfide, the same chemical that makes rotten eggs smell so foul.
It rotates from east to west like Venus. Its tilt causes extreme seasons that last 20-plus years, and the sun beats down on one pole or the other for 84 Earth-years at a time.
Methane in the atmosphere gives Uranus its blue-green tint. It also has 13 sets of faint rings.
Epilepsia del lóbulo temporal
Trastornos de memoria
Trastornos del lenguaje
Trastornos de percepción visual
Agnosias auditivas
ttranstornos auditivos:
Lóbulo Temporal
Neptune is about the size of Uranus and is known for supersonic strong winds.
Neptune is far out and cold.
The planet is more than 30 times as far from the sun as Earth.
Neptune was the first planet predicted to exist by using math, before it was visually detected. Neptune is about 17 times as massive as Earth and has a rocky core.
Memoria:
centro de almacenamiento de la información,
integración sensoria multimodal: l
es el estudio de cómo la información de las diferentes modalidades sensoriales
audición:
se encuentran la cortezas auditivas primaria, secundaria y asociativa
Anatomía:
fundamental para las habilidades tan importantes como el habla o la percepción auditiva , ademas de estar mu vinculado a la efectividad, la memoria y el reconocimiento
How long does it take for Neptune to go around the sun?
Unidades funcionales
Unidad sensorial
Corteza visual
Corteza auditiva
Corteza somestésica
Corteza vestibular
Corteza gustativa
Una lesión bilateral provocaría alteraciones de la sensibilidad gustativa.
Lóbulo Occipital
Jupiter is a giant gas world that is the most massive planet in our solar system.
Its swirling clouds are colorful due to different types of trace gases.
And a major feature in its swirling clouds is the Great Red Spot, a giant storm more than 10,000 miles wide. It has raged at more than 400 mph for the last 150 years, at least.
Jupiter has a strong magnetic field, and with 75 moons, it looks a bit like a miniature solar system.
Patología
Alucinaciones visuales
Ciertas lesiones en esta área pueden causar alucinaciones e ilusiones visuales
Agnosias visuales
Se caracterizan por la incapacidad para interpretar el significado de los estímulos percibidos a través de la vista. Áreas afectadas 18 y 19
Ceguera cortical
Suelen ser causada por lesiones bioccipitales de la arteria cerebral posterior, general mente como consecuencia de un infarto cerebral; Si las dos áreas son afectadas en su totalidad se produce una ceguera real.
Escotoma
significa “oscuridad creciente” y se caracteriza por la pérdida total
de visión en la zona correspondiente al campo contralateral de ambos ojos, tras lesiones en
la corteza visual primaria, que generalmente son la consecuencia de accidentes vasculares
agudos
Áreas
Área 19
Junto con el Área 18 forma el Área de asociación visual y está situada inmediatamente
por detrás y por encima de los lóbulos parietal y temporal respectivamente. siendo el lugar donde produce la informaciones visuales y de los sistemas auditivos y sensoriales. En el Área 19 también se localizan centros responsables del control
motor ocular.
ÁREA 18
llamada regíon paraestriada, es el área visual secundaria. Relacionada con la elaboración y síntesis de información visual.
Área 17
Jupiter has a strong magnetic field, and with 75 moons, it looks a bit like a miniature solar system.
Name the 4 most known moons.
esta
Es la cara interna del lóbulo Occipital, rodea a la Cisura calcarina, Corresponde al córtex visual primario, siendo la zona donde finaliza la radiaciones ópticas procedente del tálamo que a su vez transmite la información a la retina.
Funciones
consiste en el procesamiento de información visual
Área visual terciaria
Realizan una integración visual multimodal
Área visual secundaria
integran unimodalmente las sensaciones visuales, transformándolas en perceptos visuales.
Área visual primaria
Color, brillo y movimiento de la imagen recibidas por la retinas
Tenemos 3 áreas
Definición
Ocupa el polo posterior del cerebro y es el menor de los cuatro lóbulos externos del córtex cerebral. Presenta unos límites anatómicos externos poco visibles que corresponden a los lóbulos temporales por su parte inferior y a los lóbulos parietales por su zona anterior, Según la nomenclatura utilizada por Brodmann el lóbulo occipital se divide en tres áreas
Additional info
Mars
Mars is a cold, desert-like place covered in dust. This dust is made of iron oxides, giving the planet its iconic red hue.
Mars shares similarities with Earth: It is rocky, has mountains, valleys and canyons, and storm systems ranging from localized tornado-like dust devils to planet-engulfing dust storms.
Moons
Moon name
Mars has two small moons.
Name these moons.
How long does it take for Mars to go around the sun?
A planet's day is the time it takes the planet to rotate or spin once on its axis.
Write down Mars's day measured in Earth days.
Earth
Earth is a water world, with two-thirds of the planet covered by oceans.
It's the only world known to harbor life.
Earth's atmosphere is rich in nitrogen and oxygen.
Its name originates from 'Die Erde,' the German word for 'the ground.'
Earth may once have had two moons, nowadays it has just one.
How long does it take for Earth to go around the sun?
How many hours
A planet's day is the time it takes the planet to rotate or spin once on its axis.
Write down the Earth's day in hours.
Venus
Venus is Earth's twin in size and has no moons.
Its surface has various mountains and volcanoes. Because of its thick, toxic atmosphere that's made of sulfuric acid clouds, Venus is an extreme example of the greenhouse effect. The average temperature on Venus' surface is 900 F (465 C).
Venus spins slowly from east to west, the opposite direction to most of the other planets.
The Greeks believed Venus was two different objects — one in the morning sky and another in the evening. Because it is often brighter than any other object in the sky, Venus has generated many UFO reports.
Orbit around the Sun
How many days
How long does it take for Venus to go around the sun?
Day
How many Earth days
A planet's day is the time it takes the planet to rotate or spin once on its axis.
Write down Venus's day measured in Earth days.
Position from the sun
Position
Our Solar System has eight “official” planets which orbit the Sun.
Each planet is at a different distance from the sun. Name its position.
Divisiones Funcionales de la Corteza cerebral
Mercury is the smallest, only a little bit larger than Earth's moon. Mercury has no moon.
It experiences dramatic changes in its day and night temperatures: Day temperatures can reach a scorching 840 F (450 C), which is hot enough to melt lead. Meanwhile, on the night side, temperatures drop to minus 290 F (minus 180 C).
It also has a very thin atmosphere of oxygen, sodium, hydrogen, helium, and potassium and can't break-up incoming meteors, so its surface is pockmarked with craters, just like the moon.
Áreas primarias y de asociación
c) Corteza límbica
Es la zona más primitiva del cerebro asociativo y guarda una estrecha relación con los procesos anémicos, motivacionales y emocionales
b) Corteza occípito-parieto-temporal
Se localiza en la convergencia de los tres lóbulos posteriores del cerebro
a) Corteza prefrontal
Ocupa la zona anterior del lóbulo frontal y constituye la base de los procesos de pensamiento más específicos y simbólicos de la especie humana