por Justin Fares 2 anos atrás
169
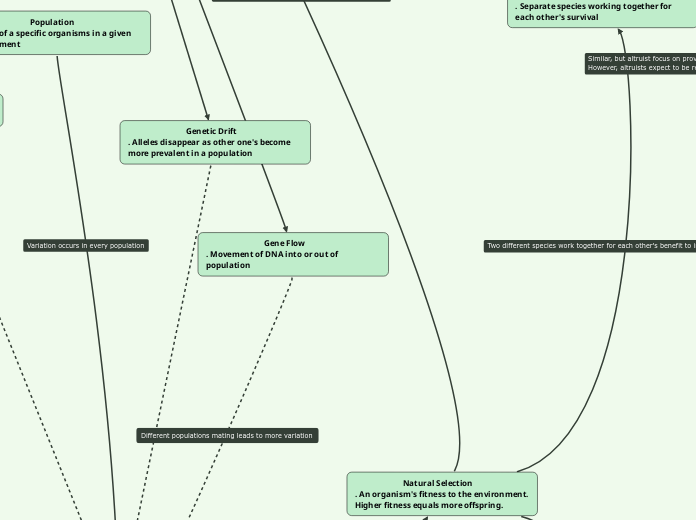
Evolutionary Concept Module 2
The document explores various biological and evolutionary concepts, focusing on how genetic and cultural traits are transmitted and evolve over time. Cultural transmission refers to the passing of traditions and behaviors from one generation to the next.