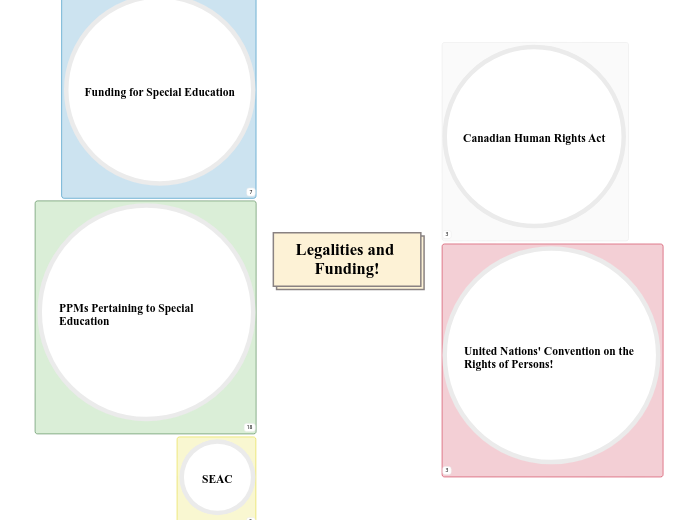
Legalities and Funding!
'Six Thinking Hats' can help you to look at problems from different perspectives, but one at a time, to avoid confusion from too many angles crowding your thinking.
SEAC
The Yellow Hat will help you to think positively. While you are 'wearing' this hat be optimistic, notice the benefits and the value in them.
School Board Obligations
Makes recommendation to board, development and delivery of special education programs and services for exceptional students
School boards have worked with government to get mental health grant
To request for funding for SEA (laptops and resources)
2. employ mental health professionals to directly support students • provide professional learning and training for educators, school-based mental health professionals, and system leaders
Legislation
Why do students not get SEA equipment within a year of request?
Legislation for SEAC dicates the extent to which the board provides special education programs and special education services and the extent to which it purchases those programs and services from the school boards
Regulation 298
-Sets out the maximum enrollment in various types of special education classes.
Covers the duties of principals, vice-principals and teachers.
Covers the qualifications of teachers.
Regulation 306
Covers the provision of special education programs and services;
Funding
Committee participates in board annual budget and reviews financial statements of the board
School boards may purchase software that increases access to the Ontario curriculum to support students with special education needs, through the SEA Per-Pupil Amount
SEA
For costs over $800.00 for pupil’s assistive devices and/or technology required for classroom instruction. Anyone can look at the “Funding GuidelinesSpecial Equipment Amount (SE
Roles and Responsibilities
Psychologist can make a recommendation to board to provide assistive technology
IS the Student success centre involved in SEA?
SEAC committee is responsible for aiding the school
They can support families with students who are creating a SEA claim with their in school team
History
When is the SEAC involved with YRDSB?
1998 SEAC revised ?https://www.ontario.ca/laws/regulation/970464?_ga=2.12837043.50473084.1637965675-20806105.1628084004
PPMs Pertaining to Special Education
The Green Hat represents creativity. Develop creative solutions to any problem with this hat. This unconstrained mindset allows you to freely test out a variety of useful creativity tools, due to its low level of criticism.
PPM 11
Policy revised in 1982 - Each school board is required to have procedures to identify each child's level of development, learning abilities and needs and to ensure that educational programs are designed to accommodate these needs and to facilitate each child's growth and development. These procedures are a part of a continuous assessment and program planning process which should be initiated from kindergarten and throughout elementary and secondary school.
PPM 59
Issued October 11, 1982 - Outlines the principles that should be taken into account when considering the provision of psychological services.
PPM 76C
Issued October 4, 1991 - Recognizes the need for flexibility in providing funding for a range of alternative placements for deaf, blind, and deaf-blind pupils who are enrolled in school board programs and who are eligible to attend a Provincial School or the Centre Jules-Léger. These include resource/withdrawal settings and self-contained classes.
PPM 81
Issued July 19 1984 - Outlines the health support services of school aged children that are not covered by the government/extend beyond educational services.
The attached chart, developed jointly by staff of the three ministries, summarizes the respective responsibilities.
PPM 85 has been consolidated and replaced by the Guidelines for Approval and Provision of an Education and Community Partnership Program (ECPP) 2020-21
PPM 85
Sets out the guidelines for Approval and Provision of an Education and Community Partnership Program (ECPP) (formerly Care and/or Treatment, Custody and Correctional Programs)
ECPPs are voluntary collaborative partnerships between Ontario district school boards and government-approved facilities such as children mental health agencies, hospitals or youth detention centres. District school boards provide the educational component (“Education Program”) while facilities provide the care and/or treatment or rehabilitation (“ECPP Services”) ECPP is only for children and youth who cannot attend schools because of their primary need for care, treatment and/or rehabilitation services
PPM 140
Issued May 17, 2007 - The purpose of this memorandum is to provide direction to school boards to support their use of applied behaviour analysis (ABA) as an effective instructional approach in the education of many students with autism spectrum disorders (ASD).
This memorandum establishes a policy framework to support incorporation of ABA methods into school boards’ practices. The use of ABA instructional approaches may also be effective for students with other special education needs.
Requirements:
1. School boards must offer students with ASD special education programs and services, including, where appropriate, special education programs using ABA methods.
2. School board staff must plan for the transition between various activities and settings involving students with ASD.
PPM 156
Issued February 1, 2013 - This memorandum sets out for school boards
and schools new requirements for transition plans for students with special education needs from Kindergarten to Grade 12.
Effective transition planning is important. Individualized transition plans that reflect a student's strengths and needs provide the foundation for successful transitional experiences.
PPM 8
Issued August 26, 2014 - This memorandum sets out requirements for school boards for the identification of and program planning for students who have learning disabilities. It provides the ministry's definition of the term learning disability, which must be used by an Identification, Placement, and Review Committee (IPRC) in the identification of students who have learning disabilities
PPM 1
Issued April 2, 1986 - Outlines services provided free of charge for school boards and agencies that have hearing impaired, visually impaired, and deaf-blind pupils in their jurisdictions.
These services are:
-Audiological services
-Psychological and assessment services
-Educational consultative services
-Professional development services
-Learning materials and media (ex: braille and audiotape materials)
Funding for Special Education
The Blue Hat thinking represents process control. When having trouble because ideas are needed, the Green Hat may come in handy since it is the one used for creativity. In case of emergencies and dealing with them, the Black Hat is required.
SEPPA
Special Education Per Pupil Amount
Allocated to boards on the basis of total enrolment
HNA
High Needs Amount
Funding for intensive staff support for students with high needs
SEA
Special Equipment Amount
For special equipment
SIP
Special Incidence Portion
Funding for students with extraordinarily high needs
FA
Facilities Amount
For school-aged children and youth in Government-approved facilities such as hospitals, custody or correctional facilities, or a care and/or treatment facility
FG
Foundation Grant
Basic level of funding for each student
SEG
Special Education Grant
Additional money for students who need special services and equipment.
United Nations' Convention on the Rights of Persons!
Using the Red Hat, you will use your intuition and emotions. Also, you will consider how others might look at the problem emotionally. Try to understand the responses of people who do not fully know your reasoning.
People can turn to the Canadian Human Rights Act to protect themselves against harassment or discrimination when based on one or more grounds of discrimination such as race, age and sexual orientation.
The Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms of 1982 is part of Canada’s Constitution. The Charter protects every Canadian’s right to be treated equally under the law.
What the Convention endeavours to do is to elaborate in detail the rights of persons with disabilities and sets out a code of implementation.
Canadian Human Rights Act
Using the white thinking hat, you center your attention around the available data. Take the information that you have, analyze it, and see what you can learn from it. Become aware of your weak points and start working on improving your knowledge.
Countries are to recognize that all persons are equal before the law, to prohibit discrimination on the basis of disability and guarantee equal legal protection (Article 5).
Countries that join in the Convention engage themselves to develop and carry out policies, laws and administrative measures for securing the rights recognized in the Convention and abolish laws, regulations, customs and practices that constitute discrimination (Article 4).
The Canadian Human Rights Act of 1977 protects people in Canada from discrimination including people with disablilties