por PB - 10BD 908819 North Park SS 3 anos atrás
779
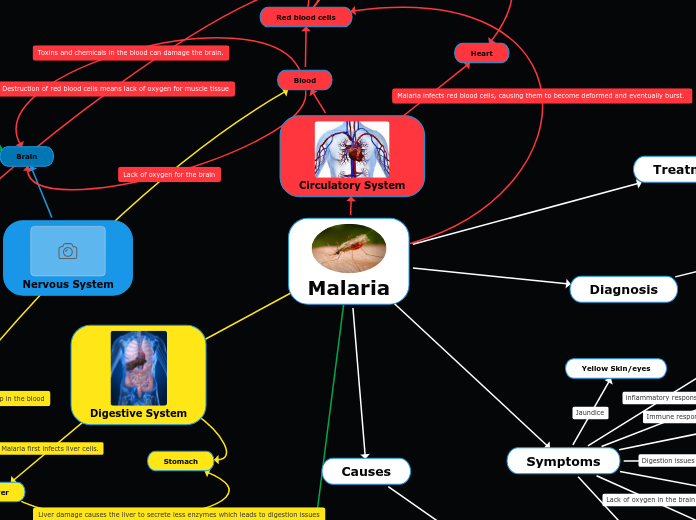
Malaria
Malaria is a disease transmitted by female Anopheles mosquitoes, which inject the Plasmodium parasite into the bloodstream during a bite. The parasite first targets liver cells, where it reproduces asexually before moving on to infect red blood cells.