numerico
Tenses demonstrate the time of actions centered around the subject of the sentence. These actions are called verbs and change according to tenses.
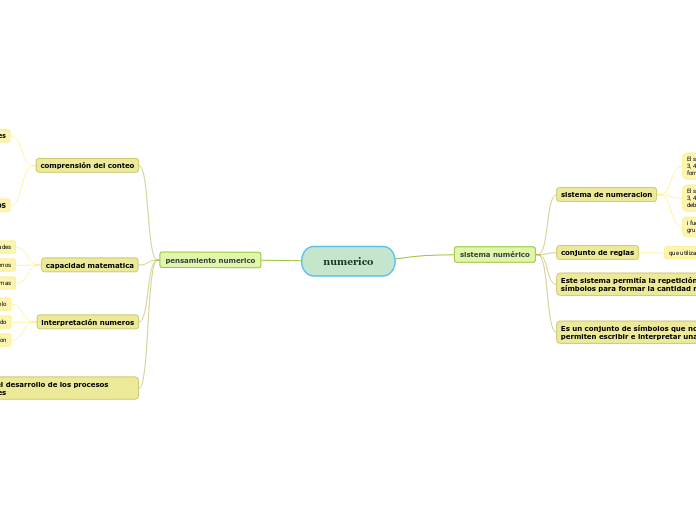
pensamiento numerico
There are four Future tenses:
- Future Simple ('with Will' and 'with Going to')
- Future Continuous
- Future Perfect Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
plantean el desarrollo de los procesos curriculares
Future Perfect Simple is used for:
- an action that will continue up until a point in the future
- an action that finishes just before another time or action in the future
Some adverbs used with Past Perfect Continuous for future actions:
- for
- since
- next week
- next month
- next year
conteo de cantidades discretas
Structure:
Will + Subject + Have Been + Verb-ING
e.g. How long will they be working on that project next week?
numeros naturales
Structure:
Subject + Won’t Have Been + Verb-ING
e.g. They won’t have been working on that project for two years next week.
como por ejemplo
Structure:
Subject + Will Have Been + Verb-ING
e.g. They will have been working on that project for two years next week.
interpretación numeros
Future Perfect Simple is used for:
- an action that will be finished by a particular time in the future
- an action that starts before and continues up to another action or time in the future
- an action that will finish before a certain time in the future, but it is not known exactly when
Adverb used with Future Continuous:
- tomorrow (e.g. tomorrow by 7)
relacion
Structure:
Will + Subject + Have + Past Participle?
e.g. Will you have met your colleague by this time tomorrow?
significado
Structure:
Subject + Won’t Have + Past Participle
e.g. I won’t have met my friend form United States by this time tomorrow.
Structure:
Subject + Will Have + Past Participle
e.g. I will have met my friend form United States by this time tomorrow.
capacidad matematica
Future Continuous is used:
- for an action that is likely to happen in the future and continue for an expected length of time
- for an action that will be in progress at some point in the future
- for action verbs (e.g. running)
- for predictions about future events
Adverb used with Future Continuous:
- tomorrow (e.g. tomorrow at 5 o'clock)
cuestionarios o problemas
Structure:
Will + Subject + Be +Verb-ING?
e.g. Will you be having fun at the party?
análisis fenomenos
Structure:
Subject + Won’t Be + Verb-ING
e.g. He won’t be having fun at the party.
realización de actividades
Structure:
Subject + Will Be + Verb-ING
e.g. You will be having fun at the party.
comprensión del conteo
Future Simple is used:
- to predict an event in the future
- to invite
- to give orders
- to express willingness
- for actions that have not yet occurred but that will occur at a future date
PLANTEAMIENTOS
'Going to' Future is used:
- to talk about our future intentions and plans
- for commands
Some adverbs used with 'Going to' Future:
- later
- tonight
- tomorrow
- next week
- next month
- next year
magnitudes
Structure:
BE + Subject + going to + Infinitive Form of Verb?
e.g. Are you going to read the whole book over the weekend?
pensamiento metrico
Structure:
Subject + BE not + going to + Infinitive Form of Verb
e.g. He isn't going to spend his vacation in Hawaii.
PROCESOS GENERALES RELATIVOS
Structure:
Subject + BE (am/is/are) + going to + Infinitive Form of Verb
e.g. She’s going to be a professional dancer when she grows up.
para empleo de actividades
Future Simple with 'will'' is used:
- to predict the future
- for something with absolute certainty
- when we're talking about a decision at the moment of speaking
- promises, requests, refusals, offers
- future facts
Some adverbs used with Future Simple:
- tomorrow
- next week
- next month
- next year
Hacer cómputos de manera fluida y hacer estimaciones razonables.
Structure:
Will + Subject + V1(First Form of Verb)?
e.g. Will you see Mary when she comes back from Denmark?
Comprender el significado de las operaciones y como se relacionan unas con otras.
Structure:
Subject + Won’t (will not) + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. You won’t see Mary when she comes back from Denmark.
Comprender los números, las formas de representarlos, las relaciones entre ellos y los sistemas numéricos
Structure:
Subject + Will + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. I will see Mary when she comes back from Denmark.
sistema numérico
There are four Present tenses:
- Present Simple
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
Es un conjunto de símbolos que nos permiten escribir e interpretar una cantidad
Present Perfect Continuous is used:
- to describe an action that started in the past and has continued up to the present
- to describe an action that has just finished
Some adverbs used with Present Perfect Continuous:
- always
- only
- never
- ever
- still
- just
descripción del numero
Structure:
Have/ has + Subject + been Verb-ING?
e.g. How long has he been learning German?
palabras
Structure:
Subject + haven’t/hasn’t been + Verb-ING
e.g. She hasn’t been playing tennis for a long time.
simbolo
Structure:
Subject + have/ has been + Verb-ING
e.g. They have been learning French for two years.
Este sistema permitía la repetición de los símbolos para formar la cantidad requerid
Present Perfect is used for:
- an action that occurred at a time which is indefinite and has its effect on the subject
- an action that occurred many times and has the possibility to occur in the present/future
- an action that began in the past and is still going on in the present
Some adverbs used with Present Perfect:
- just
- already
- yet
- for
- never/ever
- up to now
define el número de unidades que se necesitan
Structure:
Subject + haven’t (have not)/ hasn’t (has not) + Past Participle
e.g. She hasn’t finished the letter.
emitir el conteo de los elementos de un conjunto
Structure:
Subject + have/ has + Past Participle (3rd Form of the Verb)
e.g. She has finished the letter.
conjunto de reglas
Present Continuous is used to indicate the ongoing time (now).
Some adverbs used with Present Continuous:
- now, right now
- at this moment
- at the moment
- continually
- perpetually
- this year
- this season
- forever
que utilizamos para nombrar y escribir los números
Structure:
Subject + BE (am/is/are) + Verb-ING
e.g. You are eating now.
empleando la menor cantidad de palabras y símbolos. inmediatamente superior.
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb 'to be':
I am beingYou are beingHe/She/It is beingWe are beingYou are beingThey are being
Form of verb 'to have':
I am havingYou are havingHe/She/It is havingWe are havingYou are havingThey are having
sistema de numeracion
Present Simple is used for:
- habits
- general truths
- repeated actions of events
- fixed arrangements/timetables
- feelings/opinions/beliefs
- instructions.
Some adverbs used with Present Simple:
- always
- usually
- seldom
- never
- sometimes
- often
- frequently, generally
- habitually, occasionally
- once, twice
i fuese cualquier base se procede de la misma manera, haciendo grupos de elementos según la base que corresponde form
Structure:
Do + Subject (I, You, We, They)+ V1 (First Form of Verb)?
Does + Subject (He, She, It)+V1 (First Form of Verb)?
e.g. Where does he work?
El sistema de numeración en base 9 tiene 9 elementos, el 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8. Para representar cantidades en este sistema se deben formar grupos de 9 en 9.
Structure:
Subject (I, You, We, They) + do not / don’t + V1 (First Form of Verb)
Subject (He, She, It) + does not / doesn’t + V1 (First Form of Verb)
e.g. He doesn’t work in a bank.
El sistema de numeración en base 6 tiene 6 elementos, el 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 y 5. Para representar cantidades en este sistema se deben formar grupos de 6 en 6. form
Structure:
Subject (I, You, We, They) + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. I usually go jogging at weekends.
Subject (He, She, It)+ V1(First Form of Verb) + s/es
e.g. She writes every day.