Biodiversity Map
Eukarya
Fungi
-Non-motile
-Cell walls made of Chitin
-Eukaryotic
-Heterotrophs (absorb food from outside)
-Symbiotic relationships
-Spores (single reproductive cell that is released)
-Sexual and asexual reproduction
Basidiomycota
-budding or asexual
spore formation
Calvatia gigantea
Ascomycota
-fungus undergoes
budding or fission
Cordyceps
Zygomycota
-Zygospores following
gametangial fusion
Rhizopus stolonifer
-Zoospores attach and
feed off host
Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis
Plantae
-Multi-cellular
-eukaryotic
-Autotrophic
-Cell walls of cellulose
-Store food as starch
-Develop from embryos
-Live primarily in terrestrial
environments although there are exceptions
Angiosperms
-utilize flowers to attract
pollinators
dicots
Mint
monocots
lilies
Gymnosperms
-seed plants with a protected
cone over seed
Gnetophyta
Melinjo
Gingkophyta
Maidenhair tree
Cycadophyta
Sago palm
Coniferophyta
Giant sequoia
Seedless Vascular
-true roots
-waxy cuticle
-vascular tissue
Psilotophyta
Whisk Fern
Lycophyta
Stag's-horn clubmoss
Sphenophyta
Field horsetail
Pterophyta
Eagle fern
Bryophytes
-waxy cuticle
-gametangia
Bryophyta
Common liverwort
Anthocerotophyta
Phaeoceros laevis
Marchantiophyta
Crescent-cup liverwort
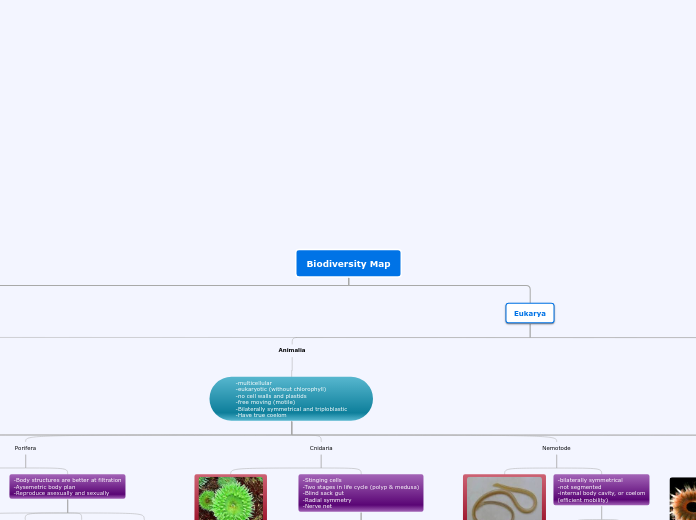
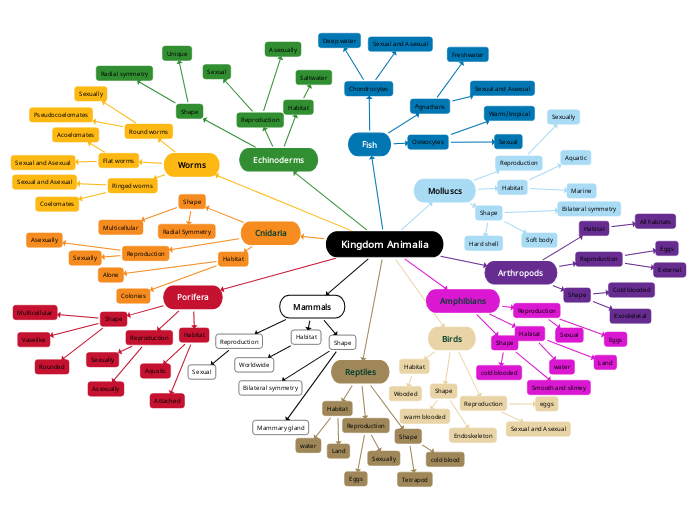
Animalia
-multicellular
-eukaryotic (without chlorophyll)
-no cell walls and plastids
-free moving (motile)
-Bilaterally symmetrical and triploblastic
-Have true coelom
Echinodermata
- bilateral symmetry (five-sided symmetry)
-echinoderm larvae are ciliated, free-swimming organisms that organize in bilateral symmetry
-They have a true coelom.
Crinoids
Sea Cucumbers
Sea star
Sea Urchin
Red sea Urchin
Chordate
-a notochord (a cartilaginous skeletal
rod supporting the body)
-a dorsal hollow nerve cord
-pharyngeal slits
-post-anal tail.
Vertebrate
Gnathostomata
Mammalia
Placentals
-Retain young in uterus
for a long time of the development
-nourished by placenta
Placentals>Marsupials
-a fetus is born smaller+less mature without placenta
-can't grow because nutrients received are limited
Monotremes
-Lay eggs
-Incubate in nest or
special pouch
Marsuplials
-Live births
-Incompletley developed fetus'
-Finish developing in pouch
Marsupials>Monotremes
-Live births instead of eggs
Aves
Reptilia
Agnathans
Amphibia
Osteichthyes
Chondrichthyes
Cephalochordates
Tunicata
Chimpanzee
Annalid
-segmented body
-tiny hair-like bristles on their outer surface called setae or chaetae
-segmentation
-well-developed body cavity.
Hirudinea
Oligochaetes
Polychaeta
Nemotode
-bilaterally symmetrical
-not segmented
-internal body cavity, or coelom
(efficient mobility)
Chromadorea
Enoplea
Ascaridida
Cnidaria
-Stinging cells
-Two stages in life cycle (polyp & medusa)
-Blind sack gut
-Radial symmetry
-Nerve net
Anthozoa
Cubozoa
Hydrozoa
Scyphozoa
Giant Green Anemone
Porifera
-Body structures are better at filtration
-Aysemetric body plan
-Reproduce asexually and sexually
Homoscleromorpha
Hexactinellida
Demospongiae
Calcarea
Spongilla lacustris
Platyhelminthes
Tapeworms
-3 germ layers
-bilateral symmetry
-primitive nervous system
Cestoda
Trematoda
Monogenea
Turbellaria
Arthopods
Silverfish
-chitinous exoskeleton
-jointed/segmented appendages
-a well-developed head and mouthparts
-striated muscles
-open circulatory system
-dorsal heart.
Crustacea
Nephropidae
Ostracoda
Maxillopoda
Malacostraca
Branchiopoda
Hexapoda
Blattodea
Protura
Insecta
Diplura
Collembola
Chelicerates
Ixodida
Pycnogonida
Merostomata
Eurypterida
Arachnida
Solifugae
Myriapoda
Chilopoda
Pauropoda
Symphyla
Diplopoda
Mollusca
Pacific oyster
-bilateral symmetry
-Unsegmented soft body with bilateral symmetry
-Presence of an internal or external shell
-A toothed tongue (made mostly of chitin) called the radula
-A mantle which is a fold in the body wall that lines the shell
-Muscular foot (and/or tentacles in some).
-Possession of a fluid-filled cavity (coelom)
Cephalopods
Bivalves
Gastropods
Protista
-Usually single celled
-Eukaryotic organism
-Heterotrophs + Autotrophs
-Digest food outside of the
body cavity
Fungus-like
-Decompose dead matter
to make energy
-Absorb nutrients
Dictyostelida
Polysphondylium
Chytridiomycota
Synchytrium endobioticum
Myxomycota
Physarum polycephalum
Oomycota
Potato late blight fungus
Animal-like
-Encircle prey and wraps around
to engulf
-Lysosomes break down the food
Spore-forming protists
-contraction of intracellular
microfilaments
Nephridiophaga blaberi
Ciliates
-Tiny cilia beat to
move through water
Paramecium caudatum
Flagellates
-Use flagellum by
rotate/whip
Pentatrichomonas hominis
Amoeba-like protists
-Locomotion using light
sensing organ
-Use pseudopodia to pull
themselves forward
Naegleria fowleri
Plant-like
-Photosynthesis
-Chloroplast
Dinoflagellates
Lingulodinium polyedra
Diatoms
Skeletonema costatum
Chrysophytes
Golden Algae
Euglenophytes
Euglena gracilis
Bacteria
-lack of membrane-
bound organelles
-unicellular (single celled)
-Prokaryote
-DNA found in plasmids
Eubacteria
-Unicellular
-Prokaryotes
-Cell membrane contains lipids
-Chromosome are circular
Spirillum
Coccus
Bacillus
Archaea
-Single celled microorganism
-Similar structure as bacteria
-Prokaryote
-Reproduce asexually
-Different DNA structure than
bacteria
Archaeabacteria
-Cell membrane contains lipids
-Flourish in the absence of Oxygen
-Rigid cell wall
-Reproduce asexually (binary fission)
Methanobrevibacter
-Found in human gut
-Cocci shape
-Consumes end products of
bacterial fermentation