por Adithya Rajesh 1 ano atrás
170
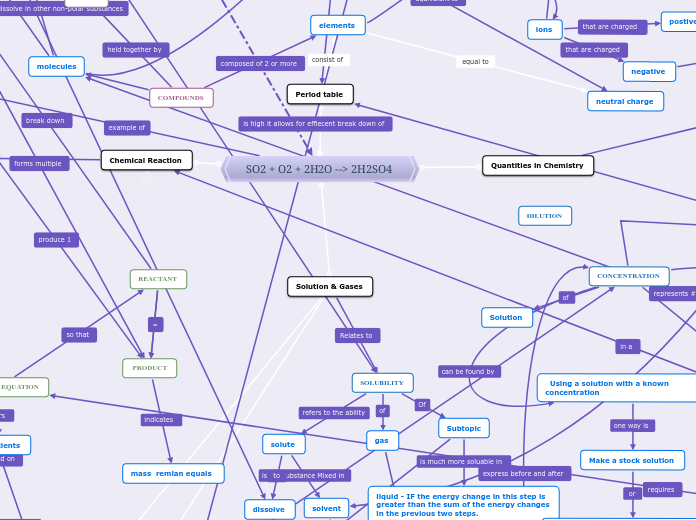
SO2 + O2 + 2H2O --> 2H2SO4
The study of chemistry involves understanding a variety of fundamental concepts and principles. These include the periodic trends and reactivity of metals, as well as the different types of chemical bonds such as ionic and covalent bonds formed between metals and non-metals.