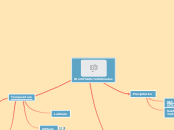
Chemistry: Preparation of Salts
Precipitation
Mix two aqueous solutions together to form the insoluble salt.
Use when salt is insoluble.
Acids Reacting With Bases
Acid + Bases --> Salt and Water
2HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 ---> Ca(NO3)2 + 2H2O
CH3COOH + NaOH ---> NaOOCCH3 + H2O
H2SO4 + 2KOH ---> K2SO4 + 2H2O
HCl + NaOH ---> NaCl + H2O
Acids Reacting With Metal Oxides
Acid + Metal Oxide --> Salt + Water
H2SO4 + CuO ---> CuSO4 + H2O
3HCl + Fe2O3 ---> FeCl3 + 3H2O
Titration
Mix two aqueous solutions of
known volume together (for complete
reaction) to form the soluble salt.
Usually between an acid and a base
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Titrate acid & base (with indicator)
Determine exact quantities that will completely
neutralise the acid & alkali.
Titrate acid & base again (without indicator)
Salt formed can then be crystallised out in pure
form.
Used when acid is soluble and if the substance being added to the acid is soluble.
Acids Reacting With Metals
EXAMPLES:
Acid + Metal --> Metal Salt + Hydrogen
2HCl + Ca → CaCl2 + H2
H2SO4 + Mg ---> MgSO4 + H2
Acids Reacting With Carbonates
Acid + Carbonate --> Salt + Carbon Dioxide + Water
2HCl + CaCO3 ---> CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O
H2SO4 + CaCO3 ---> CaSO4 + CO2 + H2O
2HNO3 + Na2CO3 ---> 2NaNO3 + CO2 + H2O