by Jacy Teo 14 years ago
2214
Chemistry: Preparation of Salts
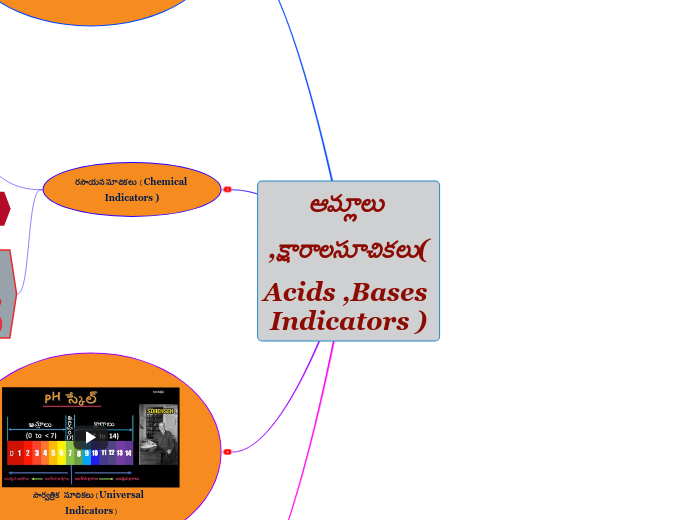
The preparation of salts in chemistry involves various methods depending on the solubility of the reactants and the desired products. Titration is utilized when both the acid and the base are soluble, allowing for the precise neutralization and subsequent crystallization of the salt.