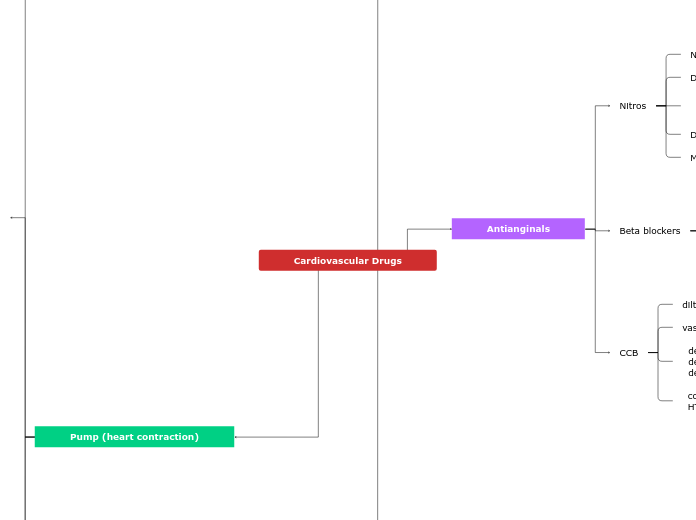
Cardiovascular Drugs
Pump (heart contraction)
Antiarrhythmics
Class IV
Tx for HTN, angina
Phase 2: block calcium channels,
delay phase 1&2
diltiazem, verapamil (CCB)
Class III
Tx for V-fib, pulseless v-tach,
cardiac arrest
Phase 3: block
K+ channels
amiodarone, sotolol
Class II
Tx for SVT, PVC
Phase 4: prolongs rest phase
decrease BP, workload
Beta blockers -lol
Class I
Tx for V-tach
Phase 0: block Na+
channels
Lidocaine, flecainide
CHF
Cardiac Glycosides
dig toxicity
check heart rate
make heart beat
slower & harder
Digoxin
PDE inhibitors
Don't give with Lasix
AE: ventricle arrhythmias
increase contraction &
increase SNS stim.
Milrinone. IV only
HCN blockers
caution w/ A-fib
& heart block
AE: bradycardia, HTN, a-fib
slows SA node
improves cardiac output
Ivabradine
AntiHTN
SNS blockers
check HR before administering
lower BP, lower HR
Block SNS response
Beta-blockers -lol
Diuretics
Pt. ed. reasons for med
& compliance
1st line med for HTN
increase Na+ & water excretion
frim kidneys
hydrochlorothiazide, spironolactone
vasodilators
monitor pt. w/ CAD, CHF, tachycardia
lower BP, causes tachycardia
used in severe HTN emergencies
hydralazine, minoxidil, nitroprusside
AE: low BP S&S
slows contractility & impulses
dilates arteries
inhibit movement of Ca+
in action potential Phase 2
-dipine
ARBs
AE: low BP S&S
renal damage
lowers BP
block angiotensin II
receptors
-sartan
ACE inhibitors
take on empty stomach
treats HTN
decrease BP
decrease aldosterone
block angiotensin-converting
enzyme=no Angiotensin II
-pril
AntihypoTN
Long term: midodrine (PO)
Short term: Norepi, epi,
phenylephrine (all IV)
Stimulate SNS response
Increase BP, blood volume,
& heart contraction
Plasma (blood)
Anemia Tx.
Epo stimulation
Monitor: HTN, seizures, Hgb level
IV or subq only
CKD, dialysis, cancer
epoetin alfa
Other anemias
Monitor GI & bone marrow
sickle cell: hydroxyurea, ABX
Megaloblastic: Folic acid, Vit. B12
iron deficiency
Diarrhea, dark stools
Z-track or PO
elevate serum iron
ferrous-
Anticoagulants
Antidotes: warfarin=Vit. K
heparin=protamine sulfate
Eliquis & Xarelto=Andexxa
PE, DVT, A-fib
Interferes w/ clotting cascade
Antiplatelets
Aspirin, Plavix, Brillinta
Good pt. teaching
Know pt. hx.
CVD, CAD, PAD
Slippery platelets
Antianginals
CCB
coronary artery spasms
HTN, angina
decrease workload
decrease HR
decrease O2 needs
vasodilation
diltiazem, verapamil, -pine
Beta blockers
Subtopic
decrease HR
decrease contractility
decrease BP
Tx. for HTN, angina
-lol, metoprolol
Nitros
Monitor HR & BP
Dizziness, headache, SOB
decrease preload
decrease workload
Dilates blood vessels
Nitroglycerin, Nitro paste
Pipes (blood vessels)
cholesterol absorp. inhibitors
bloating, cramping
Take alone. 2-4 hrs.
lower cholesterol absorption
Ezetimibe
bile acid sequesterase
Limits fat sol. Vitamin absorption
Pt. compliance issues
4-6x/day
Binds with bile
Cholestyramine
HMG-CoA
Rhabdo & cataracts
Monitor liver
Blocks cholesterol synthesis
Statins