作者:Mónica Sandoval 11 年以前
505
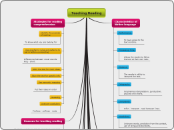
Teaching Reading
Effective reading instruction involves various strategies and principles tailored to enhance comprehension and engagement. Key strategies include using graphemic rules for decoding, distinguishing between long and short vowel sounds, identifying reading purposes, skimming for main ideas, guessing meanings, and analyzing vocabulary through prefixes, suffixes, and roots.