The Great War
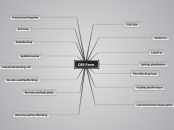
Important Persons
The No. 2 Construction Battalion
The battalion was placed in non-combat roles only
They built roads and trenches, cleared land mines and carried wounded men
The Canadian army authorized the creation of an all-black unit with white commanders
Harlem Hellfighters (American)
Henry Johnson fought off approximately 30 German soldiers with a knife in No Man's Land but didn't receive acknowledgment until 70 years later
An African-American infantry unit who spent more time in combat than any other American unit
Sir Arthur Currie
Known for his leadership during Vimy ridge
He used the tactic called 'Creeping Barrage' to take the ridge
a creeping barrage involved artillery fire moving forward in stages just ahead of the advancing infantry. To work, the strategy required precise timing by both the heavy artillery and the infantry. Failure to do this would result in the artillery killing their own soldiers
Built models of Vimy Ridge for troops to practice th attack
Issued maps of battle grounds to every soldier
Billy Bishop
He is the top ACE of the war in both the Canadian and the British Empire
Has 72 confirmed kills
Canada's top ACE
Treaty of Versailles
Imposed harsh financial, military and territorial penalties on Germany
Germany was forced to sign the
"War of Guilt Clause"
Accept responsibility for causing all the loss and damage of the war
Pay for the cost of the war and compensate the severely damaged countries (132 billion gold marks/$393.6 billion USD)
Finished paying it off on October 3 2010
Limit size of military to no more than 100,000 men and stop manufacturing large armaments
give up some European territory and overseas colonies
Agreement between Allies and Central Powers
Key Battles
Canada's 100 days
During the 100 Days, Canadian troops lead most of the
major assaults and more farther and faster than any other
army in the war.
For 100 Days, the Allies attacked all along the front and the Battle of Amiens was a complete victory. The German lines were broken and never recovered
Germans were exhausted
and almost out of supplies after Operation Michael
Lead by 100 tanks, Australians and
Canadians
Operation Michael
Germany tried two more times
but failed to strike a fatal blow
The attack pushed back the Allies but did not end the war
Germany decided to gamble
one last time by taking all of its men and made a all-or-nothing attack on the allied trenches to try to end the war before the Americans could arrive
The beginning of the end
USA had entered the war and
1,000,000 fresh troops were
coming to Europe
Russia had a Revolution
and pulled out of the war
German people were starving
at home and industry was falling
apart because of the blockade
Germany was slowly losing the
war on the battlefield
Battle of Passchendaele (July 31-November 10 1917)
Using a series of small attacks, the
Canadians were victorious
Right from the start of this battle, there was terrible weather (Quagmire)
Battle of Vimy Ridge (April 9-April 12 1917)
Canadians took the ridge in only a few hours
Thanks to victory, the Canadian army were now known as "Shock Troops" and an elite task force
The battle was led by Sir Arthur Currie
Canadians were tasked with capturing Vimy Ridge
Battle of Somme (July 1-November 18 1916)
It known as the bloodiest battle in human history
1.5 million men were killed including 24,000 Canadians
The battle was a huge disaster and pointless
Battle of Ypres (April 22-May 25 1915)
This was the first major battle fought by Canadians
No ground gained for either side
A war of attrition (many casualties)
Warfare
Air
ACE
Billy Bishop is known as Canada's top ACE
If a fighter pilot shot down five or more enemy aircraft, they were known as ACEs
Canada's involvement
By the end of the war, 40% of pilots for the Allies were Canadian
About 22,800 Canadians served as pilots, gunners, mechanics and aircrew
The use
Later progressed into using them to drop bombs and fire at the enemy
The initial use for airplanes was to use them to fly over enemy lines to take pictures and gather information
Sea
Lusitania
America joined the war changing history
Half of the passengers died as a result including 128 Americans
A major turning point in the war as it drastically changed the public opinion of the war for Americans
A British passenger also carrying war supplies to Britain that was torpedoed in 1915
U-Boats (submarines)
They could attack without warning and disappear without detection
Used by Germans to cut off Britain's supplies as they attacked supply ships heading towards Britain
Importance
It became an important for both sides to try and sink as many of the enemy supply ships as possible
Both Britain and Germany relied on ships to supply food, raw materials, medical equipment, soldiers and weapons
Halifax Explosion
The Effects
The explosion was the most devastating disaster on Canadian soil and was the largest man-made explosion the world had seen at the time
A pressure wave snapped trees, bent iron rails, demolished buildings, grounded vessels (including Imo which was washed ashore by a tsunami) and scattered fragments of Mont-Blanc for km
Nearly all structures within an 800m (half-mile) radius, including the community of Richmond were obliterated
Six square km of Halifax was wiped out. The explosion killed 2,000 people and wounded another 9,000
The Explosion
People standing close to shore were propelled through the air, sucked up in a strange whirlwind and dropped around 10m away
Some were vapourized by the force of the explosion, others lost their eyes when windows shattered
Shards of iron, wood and steel flew in all directions including the shaft of the ship's anchor, weighing more than a half-tonne
Windows were broken from 75 km away, and the shock wave felt more than 300 km away
At 9:04am the Mont-Blanc exploded
The Crash
December 6 1917 at 8:45am they collided
A small craft forced Imo to change course, putting it in the path of the Mont-Blanc and both ships blasted their horns in warning
The Mont-Blanc a French vessel was approaching from the opposite direction
The Norwegian ship Imo was leaving the Halifax Harbour carrying much-needed war supplies
Extremely important to both sides during the war
Land
Weapons
Mines/Hand grenades and other bombs
Tanks
Machine Guns
Gas Attacks
Over the Top
The order "Over the Top" forced men to get out of their trenches, travel in the open across No Man's Land and attempt to capture an enemies trench
Soldiers were expected to dig and rebuild trenches each night, and "SAPs" (listening posts) into No Man's Land and violently defend their trench in case of attack
No Man's Land
Most men who were killed here were left unburied and the smell of death spread for miles in each direction
Entering No Man's Land was almost certain death
The open land between enemy trenches
Trench Foot
If not treated properly or quick enough, it could result in amputation
A serious condition which rotted the flesh of the feet caused when soldiers fought in cold, wet conditions in trenches without the extra socks or boots to help keep their feet dry
Life in Trenches
There was a constant fear for soldiers because of the relentless and frequent attacks they faced
Uniforms were often soaking wet, filthy with mud and infested with lice
soldiers endured bone-chilling cold, unbearable heat, or constant rain and mud depending on the time of year
Life in the trenches was overall miserable and dangerous for all sisters
Trench Warfare
The British and French soon built trenches out of necessity
Trenches were easily defended and almost impenetrable
Trenches were originally lined with barbed wire and machine guns nests and were supported by heavy cannons, later sandbags also lined the trenches and tunnels were dug and underground dugouts were built
Trenches are long, thin holes in the ground that would protect soldiers from gun fire, first built by Germans
The Schlieffen Plan
How it failed
instead of a short, surprising attack as planned, Germany's attack on France became a long, costly, and horrible beginning to trench warfare
Germans found themselves fighting France, Britain, and their Empires in the Western front
Reality
Germans were met by the French at the Battle of Marne which halted their advance
Germany didn't take the chance to take Paris, but they attacked the east of the Capital
Russia mobilized in only 10 days and Germany was forced to withdraw troops from the Schlieffen Plan to defend the Eastern border
Germans were held up by the Belgian army, backed up by the British Expeditionary Force which arrived extremely quickly
Expectations
Britain would remain neutral based on a 70 year treaty with Belgium
Belgium would not resist any German attack
France would be easily defeated in 6 weeks due to surprise
Russia would take at least 6 weeks to mobilize (prepare and organize troops for active service)
Causes of WWI
Trigger
The assassination of the Arch Duke of Austria Franz Ferdinand
M.A.I.N
Nationalism
Extreme pride and willingness to sacrifice for your country
A belief that people of similar should be united
Imperialism
Austria expanded its Empire by conquering much of the Balkans
England and France were becoming very rich because of their colonies and were threatened by Germany because they wanted colonies as well
European nations were trying to build Empires by conquering other nations (Africa and Asia)
Alliance System
Triple Entente
Russia
France
Great-Britain
Triple Alliance
Austria-Hungary
Italy
Germany
Militarism
Attempting to solve political threats through threats, brinkmanship (almost going to war) and war
A way of making Governmental decisions