Effects analysis (what for?)
Audience analysis (who?)
Analysis of the medium (how?)
Content analysis (what)
Control analysis (who?)
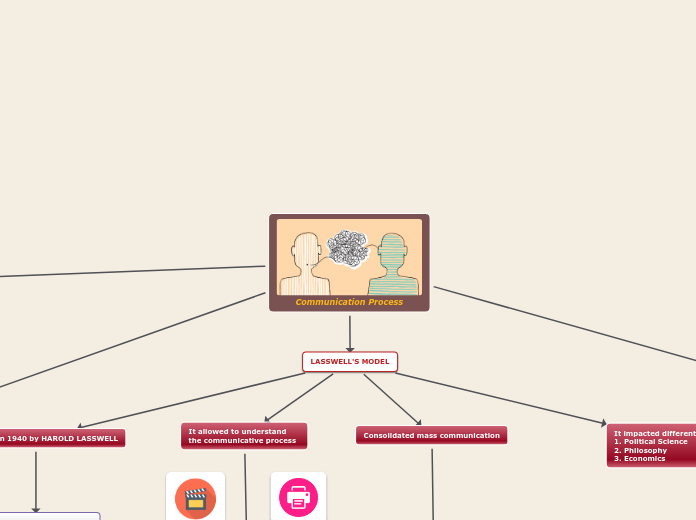
Communication Process
Communication Ability
Basic communicative abilities
Respect
Persuasion
Credibility
Read and write
Verbal language
Non-verbal language
Active listening
Empathy
Emotional validation
Benefits
Impact of this abiliity
In our self-esteem
Career success
In personal relationships
Helps to promote confidence
Helps to resolve differences
COMMUNICATION BARRIERS
HOW TO DETECT THEM?
HOW TO OVERCOME THEM?
Etc.
Verify
Active listening
Empathize
Ask
Clarify
The way of expressing oneself
Non-verbal language
Tone of voice
Administrative barriers
Physical barriers
Impersonal communication
Semantic distortions
Lack of planning
Loss of information
Information overload
Physiological barriers
States that alter communication:
Confused
Deranged
Drunk
Psychological barriers
Prejudices also play a causal role
Emotional states
Semantic barriers
From the listener
From the speaker
CASTELLS' MODEL
The network society
Conectivity
Media Autonomy
Dimensions of autonomy
Physical
Socio-political
Communicative
Professional
Corporate
Individual
Mass self-communication
Self-generated message
Mass communication
LASSWELL'S MODEL
It impacted different disciplines such as:
1. Political Science
2. Philosophy
3. Economics
Consolidated mass communication
Purposses
Impact
Interpret
Inform
It allowed to understand the communicative process
Unilateral communication
Recent events
Global events
It is composed by:
Connectivity and society
Developed in 1940 by HAROLD LASSWELL
Reduce communication gaps
Between civil society and government
COMMUNICATION ANALYSIS LEVELS