arabera Montoya Tobón Montoya Tobón 4 years ago
335
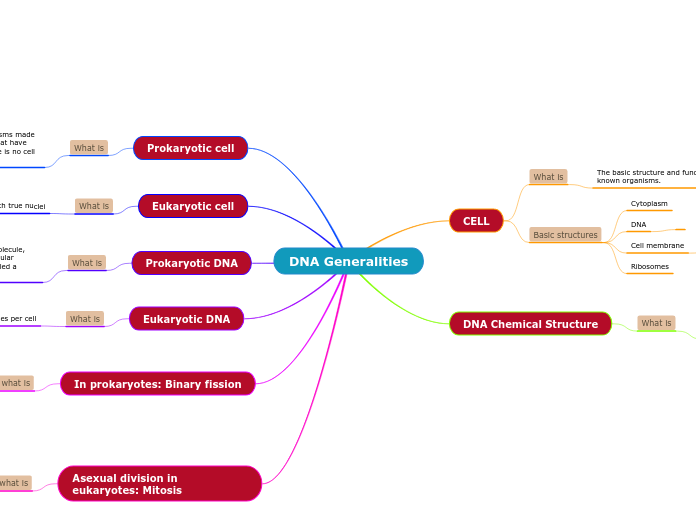
DNA Generalities
DNA is a fundamental molecule found in all living organisms, playing a crucial role in genetic information storage and transmission. In prokaryotic cells, DNA typically exists as a single, double-stranded circular molecule located in a region known as the nucleoid.