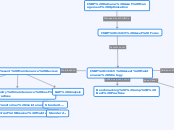
IAS 38 (Intangible Assets)
Type in the name of your subject.
Measurement after initial recognition
Add detailed notes about each lecture, so that when the time comes to prepare for exams, you will have an easier and quicker overview.
Revaluation model
Not further discussed as very rare and only possible for intangibles for which there exists an active market
Add a short description of your homework and any details you need in order to understand and complete the task.
Revalued amount less accumulated amortisation and impairment losses
Cost model
Cost less accumulated amortisation and impairment losses
Add a list of questions to help you recap your lecture.
Cost model
Add here all the details about your projects.
Residual value
Assumed to be zero, unless
Commitment by a third party to purchase or active market and
− It is probable that such a market will exist at the end of the useful life
- Residual value can be determined by reference to that market
Useful life
Factors to be considered when determining the useful life
- The expected usage of the asset by the entity and whether the asset could be managed efficiently by another management team
- Typical product life cycles for the asset and public information on estimates of useful lives of similar assets that are used in a similar way
- Technical, technological, commercial or other types of obsolescence
- The stability of the industry in which the asset operates and changes in the market demand for the products or services output from the asset
- Expected actions by competitors or potential competitors
- The level of maintenance expenditure required to obtain the expected future economic benefits from the asset and the entity’s ability and intention to reach such a level
- The period of control over the asset and legal or similar limits on the use of the asset
- Whether the useful life of the asset is dependent on the useful life of other assets of the entity
Review at the end of each financial year-end
Add the team members.
Change in accounting estimate accounted for prospectively
Finite useful life
Add a short project description.
Allocation of the depreciable amount (= cost – residual value) on a systematic basis over the useful life
Indefinite useful life
Add the project name.
No amortisation, but annual test of impairment according to IAS 36 (Impairment of Assets)
Cost model – amortization method
Schedule your course ahead. Knowing all the information will make everything easier.
Amortisation ceases when
The asset is classified as held for sale in accordance with IFRS 5 – Non-current Assets held for Sale and Discontinued Operations or the asset is derecognised
Amortisation begins when the asset is available for use
Amortisation charge recognised in P&L
Add the class information for each week.
Retirements and disposals
Gains or losses on disposal
Proceeds less carrying amount
Elimination from balance sheet when
Disposed of or no future economic benefits are expected from its use or disposal
Some remarks
Add key information about the books you've read. If you feel it's necessary, you can add a small summary of your readings in the Notes section.
IAS 38 requires to expense (passer en charge)
Training costs
Advertising costs
Relocation costs
Start-up costs
Development expenses
In some cases no material further development expenses are to be incurred from the moment all criteria to capitalise were met
In pharma and life sciences industry it is very rare that development expenses are capitalized (technical feasibility criterion)
Intangibles acquired in
a business combination
The fact that the acquirer has no intention to further use these intangibles is not a reason not to recognize them at fair value
Intention not to use has no
impact on initial fair value
In process R&D to be
recognised as well
Add summary of the content of a book
Recognition and initial measurement
Review your resource requirements and tick off the devices you will need as well as their availability. Add others, if necessary.
Specific principles
Internally generated intangible assets
Expense to P&L
Development expenses
Capitalisation of development costs if, and only if
−All these criteria are met :
− technical feasibility
− intention to complete
− ability to use or sell the asset
− probability of future economic benefits
− availability of resources (technical, financial)
− expenditure can be reliably measured
Research expenses
Examples of research activities :
• Gaining new knowledge
• Search for applications of research findings
• Search for alternatives to materials, products, processes, etc.
• Formulation, design, evaluation and selection of possible alternatives for new or improved materials, products, processes, etc.
All expenditure on research should be expensed when incurred
None of intangible asset arising form research (or research phase) should be recognised
Internally generated goodwill
Not recognised as an asset (expense to P&L)
Acquisition in a business combination
At fair value based on
− Quoted market prices (active market)
− If no active market, use techniques to estimate fair value
• multiples/profitability
• discounted future cash flows...
Reliable measurement => always considered to be satisfied
Acquired in a separate acquisition
Measurement
Expenditures that are not part of the cost of an intangible asset
− Costs of introducing a new product or service (incl. advertising and promotional activities)
− Costs of conducting business in a new location or with a new class of customers (including costs of staff training) and administration and other general overhead costs
Cost components when purchased
− Purchase price, import duties and purchase taxes, directly attributable expenditure of preparing the asset for its use
and less trade discounts & rebates
At cost
Recognition
Reliable measurement => usually satisfied (particularly when payment is in monetary assets)
Probability criterion => always satisfied
An asset meeting the definition of an intangible asset should be recognised when
Select as needed:
It is probable that future economic benefits associated with asset will flow to the enterprise and cost of asset can be measured reliably
Definition
Type in all the info you would like to know about this subject. If there is something you don't know yet, no problem! You can fill in the blanks along the way.
Aller voir le slide 48 semaine 2
Did your teacher present the objectives of this course? Write them down and add anything else that might help you reach these objectives.
Examples : ➢ Computer software
➢ Patents
➢ Motion picture films
➢ Import quotas
Add details about your teachers' evaluation criteria. This way you will know the aspects you need to focus on.