Chordates
Birds, Amphibians, Fish, and reptiles
Vertabrata
Gnathostomata
Large, jawed animals
Jaws help catch prey by gripping onto them
Multi chambered hearts, amniotic eggs, water tight skin help retain water on land
Amphibia
2 chambered heart young develop 3 chambered heart as adults
Water and land
Rhinella Marina
Reptilia
Claws
Internal skeleton and fertilization
Scales on exterior
Python regius
Aves
Hollow bones
4 chambered hearts
feathers
Erithacus Rubicula
Mammalia
Hair
Mammary glands (Milk production)
3 middle ear bones
4 chamber hearts
Monotremes
Lay eggs
Monotremata
Platypus
Marsupials
Fetus is small and immature
Marsupialia
Most young carried in a pouch
Opossum
Placentals
Have a placenta to provide nourishment to developing young
Lagomorpha
Powerful hind legs
Hares
Tetrapoda
Amniotes
Agnathans
Jawless fish
Suck for food
Hagfish
Lampreys
Echinoderms
Deutrosomes
Radial, sort of
Sea urchins
Starfish
Bivalva
Clams
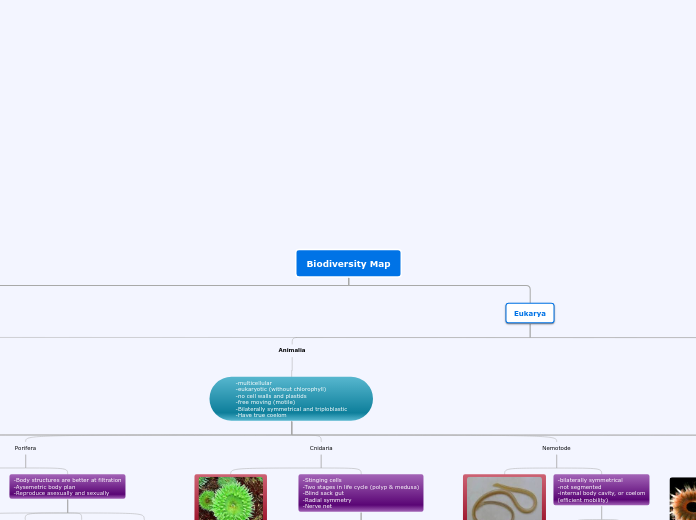
Animalia
Embryonic development stage: Blastula
Heterotrophic
Motile (Mostly)
Mollusks
Shells
Foot
Mantle
Coelom
Cephalopoda
Octopus
Gastropoda
Snails
Arthropoda
Jointed appendages
Exoskeleton (chitin)
Molts
Chelicerate
Scorpionidae
Aranae
Spiders (Arachnids)
Uniramia
Hexapoda
Insects
Bees
Diplopoda
Millipedes
Chilopoda
Centipede
Crustacea
crabs
Trilobita
Extinct
Annelida
Complete digestive tract
segmentation
Closed circulatory system
Earthworms
Leeches
Nematoda
Round worms
Complete digestive structure
Platyhelminthes
Bilateral
3 germ layers
Cephalization
incomplete digestive structure
Cestoda
Tapeworms
Trematoda
Flatworms
Subtopic
Cnidaria
Incomplete digestive systems
Radially symmetrical
No mouth or nervous systems
Scyphozoa
The true jellyfish
Hydrozoa
Fire Corals
Cubozoa
Box Jellyfish
Anthozoa
Sea Anemones/ Corals
Porifera
Filter feed
Sponges
Asexual reproduction
Asymmetry
Sessile
Plantae
Photosynthetic
Sexual fusion reproduction
Develop from embryos
Angiosperms
Flowering plants
Attract other animals to help spread seeds on land and fertilize.
Flowering Plants
P. Anthophyta
Magnolia grandiflora
Gymnosperms
Naked seeds
Conifer plants adaptation: Needle leaves reduce S.A., conserving water.
ginkgo
P. Ginkophyta
Ginkgo biloba
gnetophyta
P. Gnetophyta
Gnetum gnemon
Cycads
P. Cycadophyta
Cycus revoluta
Conifers
P. Coniferophyta
Scots pine
Seedless Vascular
Ferns
Leaves called fronds
Vascular tissue and roots for land survivability
Ferns
P. Pterophyta
Pteridium aquilinum
Club mosses
P. Lycophyta
Bryophytes
Live in moist habitats to retain moisture out of water
Lack vascular tissue
Hornworts
P. Anthocerophyta
Liverworts
P. Hepaticophyta
Mosses
P. Bryophyta
Fungi
Chemoheterotrophic
Cell walls composed of chitin
Both sexual and asexual reproduction
Deuteromycota
(Disease-causing)
Asexually reproduction only has been observed.
Produce asexual spores through sporogenesis
Aspergillus niger
Basidiomycota
Mushrooms
Reproduction takes place in the "fruiting body"
False Truffle
Zygomycota
(Bread Mould) Gametangial fusion developing into a zygospore
Rhizomes Stolonifer
Ascomycota
(Yeast)
Asexual reproduction
Reproduce through budding
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Domain
Kingdoms
Phylums
Subphylum
Classes
Groups
Order
Clade
Superclasses
Protista
Heterotrophic or autotrophic
Mostly unicellular.
All are aquatic.
Motile by flagella, pseudopods, or cilia.
NOT animals, plants, or fungi.
Fungal-like Protists
Saprophytic Heterotrophs:
Digest the food externally and absorb the nutrients.
Water Molds
Plant-like Protists
Autotrophic. Can internally nourish themselves by photosynthesis.
Rhodophyta
Red algae
Euglenoids
Euglena
Animal-like protists
Heterotrophic. Hunt other micro-organisms for nutrition.
Sporozoan
Plasmodium
Not motile: Lives in the gut of a mosquito
Flagellates
Trypanosome gambiense
Flagella for movement. Rotor-like whipping motion
Ciliates
Paramecium caudatum
Move with cilia (act like oars in water. Very fast)
Sarcodines
Amoeba Proteus
Move with pseudopods (False feet)
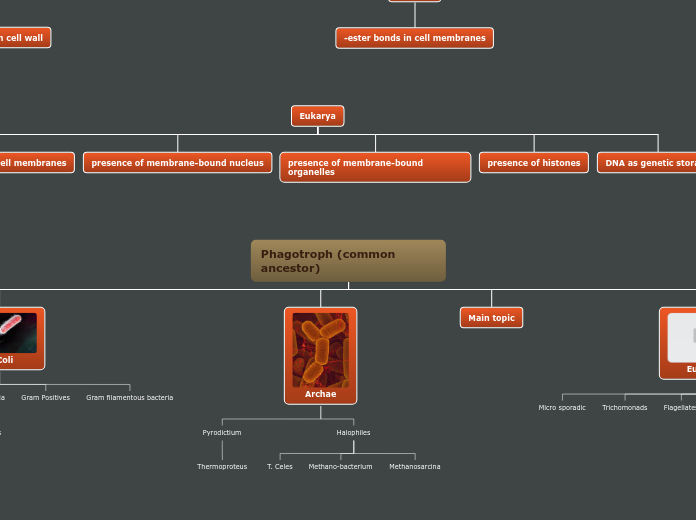
Archaebacteria
Archaea with the ability to survive some of the most extreme environments in the world (Extreme cold, hot, dry, acidic). Prokaryotic.
Crenarchaeota
Eubacteria
Prokaryotes: Simple organisms with no nucleus. No membrane-bound organelles.
Morphology:
Coccus: (Round) ~Staphylococcus
Bacillus: (Rod) ~ Hay Bacillus
Spirillum: (Spiral) ~Campylobacter jejuni
3 Domains of Life
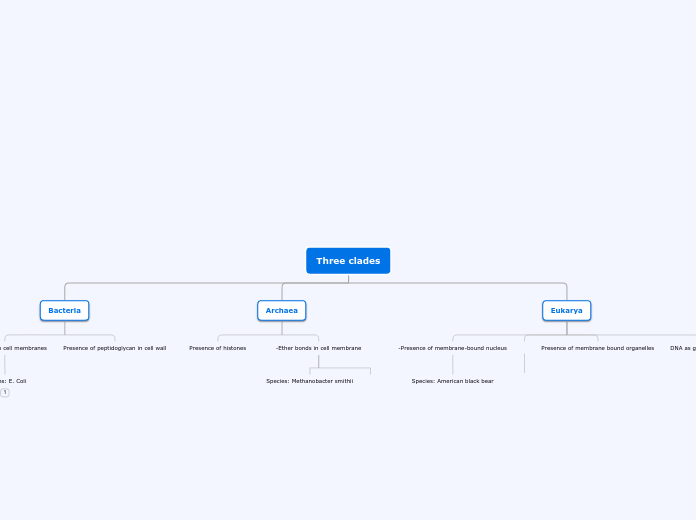
Bacteria
Prokaryotes: Any and all bacteria that are not Archaea Bacteria
Single celled-No nucleus-asexual reproduction
Archaea
Prokaryotes: Oldest domain, an ancient type of bacteria.
No nucleus-not complex-similar to eukarya
Eukarya
Eukaryotes and have membrane-bound organelles with complex structures.