Chapter 15
Golgi Apparatus
an organelle that acts as a mid way station for proteins
Dynamin
another protein that assists in vesicles formation
Transmembrane Protteins
Stop transfer sequence
contains an additional hydrophobic
stops the protein transfer through membrane
Ran - GTP
binds to nuclear import protein which allows release of the protein
nuclear import receptors
shuttle the protein across the membrane
Nuclear pores
where proteins and molecules can enter and leave the nucleus
The ER
CONTAINS UNIQUE SIGNAL SEQUENCE
Protein movemment
transport from the cytosol into nucleus
movement across membrane bound organelles
translation
polypeptide chains are synthesized by free ribosomes
Chapter 16
Positive Feedback
Negative Feedback
more activating once activated
activator is turned off once enough are activated
Cyclic AMP
Lead to gene expression
by activating other proteins
Acetylocholine
induces different
responses in multiple cells
3 type of cell surface receptors
ion channel
G-protein
Enzyme
Endocrine
Paracrine
Synaptic
Contact Dependent
Long distance signaling
local signaling
between nerve signaling
Short range signaling
Calmodium
Targets Ca2+/CDPK
Enzyme coupled receptors
when activated found in dimers
phosphorylate each other
other proteins can now bind
kinase domains pho
Floating topic
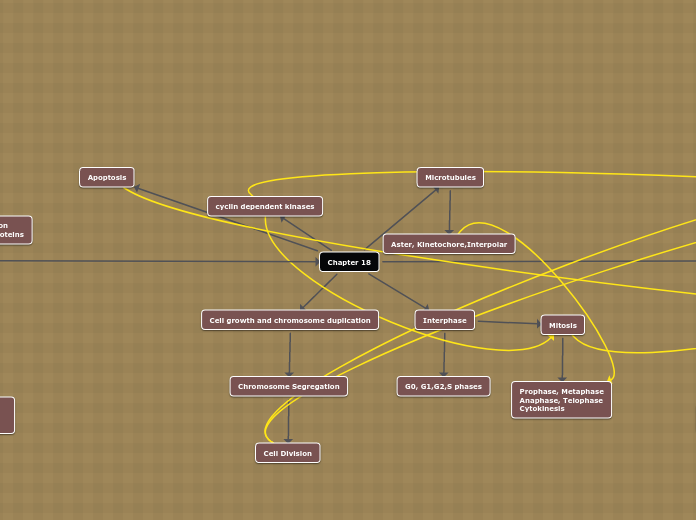
Chapter 18
Apoptosis
Microtubules
Aster, Kinetochore,Interpolar
cyclin dependent kinases
Interphase
Prophase, Metaphase
Anaphase, Telophase
Cytokinesis
G0, G1,G2,S phases
Cell growth and chromosome duplication
Chromosome Segregation
Cell Division
Chapter 19
Sexual Offspring
mixing of DNA
resulting in offspring
Asexual Reproduction
genetically identical offspring
Bivalent Chromosomes
pairs that line up
during meiosis
Mitosis
produces two identical diploid cells
Meiosis
produces four haploid cells
that are not identical
Crossing over
non sister chromosomes on bivalent chromosomes
Causes genetic variation
Chapter 20
Undergo angiogenesis
Form new blood vessels
Undergo Metastasis
Original tumor easily fragment
Characteristics of Cancer Cells
Lack differentiation:
Cells are non-specialized
Cells are immortal-enter cell cycle repeatedly
Have abnormal nuclei
Cells enlarged
Abnormal # of chromosomes
Extra copies of genes
Don’t go through apoptosis
Form Tumors
CANCER
1 in 5 people die from cancer (USA)
Cancer is the uncontrollable growth of a tissue,metastasis
Therapeutic Cloning
Crispr is an example of a process to use for gene therapy
Stem Cells
Order of freedom: Totipotent>Pluripotent>Multipotent
Tissue turnover rate
Once nervous cells are born they never die of
Intestinal cells turnover every 3-6 days
Bones take about 10 years
Tissue Communication:
Cell Communication-ex neurons
Selective Cell Adhesion- ex: epithelial sheets
Cell memory- ex. Replication