by Paxton Gunn 6 years ago
220
Macromolecules-Paxton Gunn
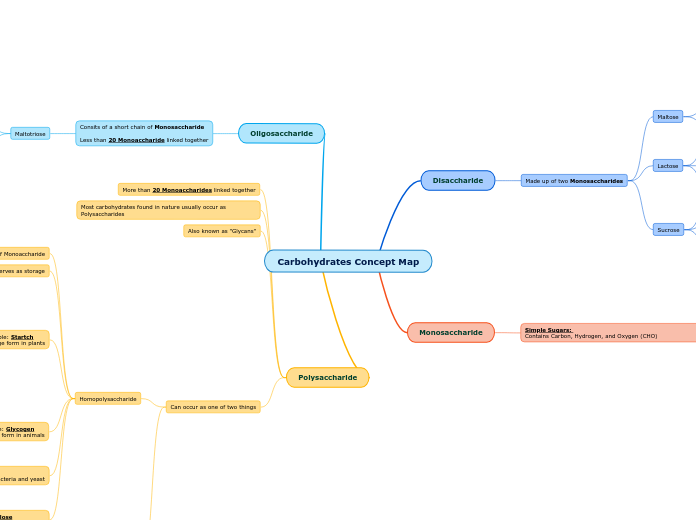
The text explores the four major types of macromolecules essential to life: proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates. Proteins, composed of amino acids, are crucial for building and repairing tissues and exhibit unique structures like helices and pleated sheets.