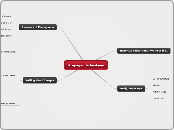
Interdependence of Three Generations
“Self defeating imbalances that would result from the excessive prioritization of any one generation over another”.
A single generation can't be emphasized more than another, without jeopardizing what is represented by the type of generation that is being privileged.
So thoroughly interconnected that it's difficult to conceive them as operating properly as anything but a supportive manner
Progressive scholars believe
the three generations
are deeply interdependent
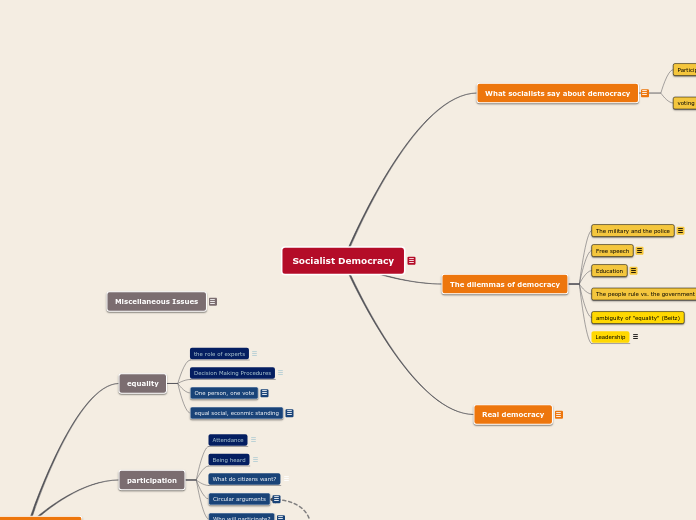
Three Generations of Human Rights Summary
Collective-Developmental
Rights have gained acknowledgement in international treaties, but are the most debated and lack political & legal recognition.
Rights of peoples and groups held against their respective states (mutual support within a group, shared interests)
Certain special rights of ethnic and religious minorities
the enjoyment of one’s own culture,
languages, religions, etc
Self-determination of peoples
their political status, cultural, economic,
and social development, etc
Civil-Political
Rights are legitimated and given status in international laws
Participation and freedom in political life
Rights are strongly independent, negatively built
to protect individuals from the state
Freedoms and Empowerments
freedom of thought and religion,
political participation in society, etc.
Physical and Civil security
no torture, no slavery, equality before the law, etc.
Socio-Economic
Rights were recognized by government after WW11
Places duty onto government to meet and fulfil individual human rights
Rights that guarantee equal conditions and treatment
Standards relating to
Providing goods that meet economic needs
work and fair wages, adequate living standards,
social security networks, etc.
Providing goods that meet social needs
shelter, healthcare, nutrition, education, etc.
Division of human rights into three generations was introduced by Czech jurist Karel Vasak in 1979.
-The three categories compare to the three principles of the French Revolution: Liberty, Equality, and Fraternity.
Challenges us to our own assumptions about rights involved in the application of human rights.
Framework is a valuable conceptual tool for thinking about human rights, although it contains room for many key debates about the nature of rights.