Vascular Bundle
Conducting vessels made of phloem and xylem (typically xylem inside phloem outside)
1000μm = 1mm
1000mm = 1m
Biology Study
Carries photosynthesis products (sugars)
Carries water and minerals
Ground
Does photosynthesis (6CO2+H2O
-light energy-> C6H12O6 + 6O2 )
Support cells
Protect on surface
Connective
Fat
Conserve heat, broken down for cellular respiration
Bone
Provide rigid bodily structure
Blood
White
Fight infection & disease
Red
Carry O2 and CO2
Neurons
Transmit electrochemical messages
Epithelial
Columnar
Secretes things (e.g mucus, stomach acid)
Protect cells underneaths
Cardiac
Pump blood from heart, involuntary
Smooth
Contracts to move things through
body (e.g air & food), involuntary
Contract to move bones, under voluntary control
Microscope
Ocular lens
10x
High power objective
40x
.4mm approx. diametre
Medium power objective
2mm approx. diametre
Low power objective
4x
4mm approx. diametre
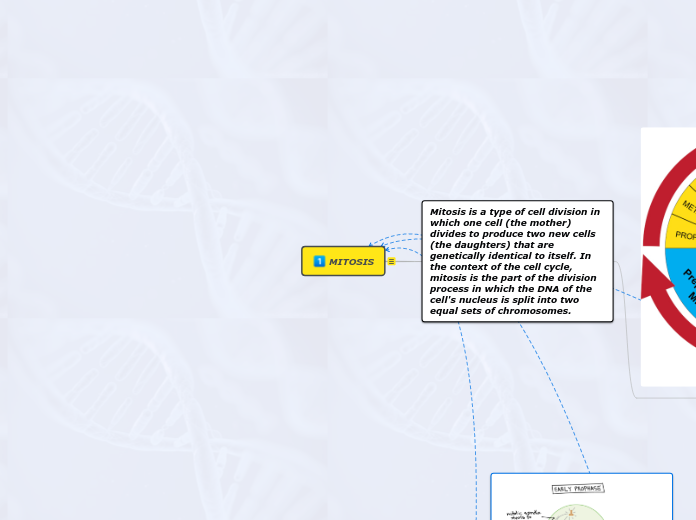
Cell Division
Ways in which it fucks up
Shtty metaphase
Not pulled apart properly
Less chromosomes
Not enough genetic information
Doesn't know how to function, dies
More chromosomes
Hard to grow, mutations happen
Deadly mutation cause cell death
Purpose
Replace / Repair
Cells die - need replacements
Grow
Be big and strong
Process
Cytokinesis
Plant
Cell plate forms
Permanent neighbors :)
Animal
Cleavage furrow forms and separates
Mitosis
Telophase
Nucleolus reappears
Nuclear membranes start reforming
Spindle fibers dissapears
Cell begins to get stretched
Anaphase
Chromatids arrive at poles
Spindles pull sister chromatids apart forming
identical daughter chromosomes
Metaphase
Spindle fibers attach to sister chromatids
Chromatids line up along the metaphase plate (imaginary)
ANIMAL CELLS: Centromeres arrive at poles
Prophase
ANIMAL CELLS: Centromeres start moveing
Nuclear membrane breaks down
Nucleolus dissapears
Spindle fiber created on centromeres
Chromatin coils and turns in to sister chromatids
Interphase
G2
Makes organelles and proteins
S
Double DNA in nucleus
G1
Checkpoint
Stop and fix, if can't commence apoptosis
Makes organelles and grows
Organelles
Smooth ER
Contain enzymes for synthesis lipids
Rough ER
Ribosomes on the surface and involved in protein synthesis
Cytoskeleton
Gives eukaryotic cells there shape and involved in movement
Contain the genetic information that is passed
from one generation of cells to the next
Complex of DNA and protein that package long DNA molecules
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
Chloroplasts
PLANT CELL: Captures energy from the
sunlight and uses it to produce food
Golgi Apparatus
Receives proteins & materials from the ER,
packages them, & distributes them
Vacuoles
Stores food, water, wastes and other materials in plant cells
Cell Wall
PLANT CELL: Rigid outer layer
Cell Membrane
Bilayer membrane of lipids that controls
what comes into and out of a cell
Nucleus
Contain DNA, which controls the functions
of the cell and production of proteins
Ribosomes
Assembles amino acids to create proteins
Lysosomes
Uses chemical to break down food and worn out cell parts
Mitochondria
Produces the energy a cell needs to carry out its functions
Centrioles
ANIMAL CELLS: Located near the nucleus and
help pull chromatids apart during cell division
Nuclear membrane
Membrane of lipids that encloses the nucleoplasm
Controls the flow of materials in and out of the nucleus
Cytosol
Gel-like fluid where organelles are found
Plant Systems
Shoot
Flower
Reproduce
Pollen from stamen to pistil - Reach egg at stigma
Stores sugars, makes colours
Buds, minimal
Stems
Fuction
Transport water and nutrients
Support leaves
Phloem
Brings sugars from sources (high conc.)
to sinks (low conc.)
Methods
Negative pressure
Transpiration pull
Column of water in xylem, when molecule of
water is used it creates a -ve gap. The one
underneath fills it's spot
up to the top
Possitive pressure
Capillary action
Water attracted to xylem, stays together with surface tension
up to 1-2m
Root pressure
Osmotic pressure in root cells
up to 30cm
Carry water
Green stems
Keep plant upright and tall to allow it to compete for sunlight
Protect plat
Fuzz with toxin
Spikes
Leaf
Perform photosynthesis to create fuel
Move produced C6H12O6 to places where growth needed
Brings H2O for photsynthesis
Mesophyll cells
Spongy
Has spaces to keep gases, behind surface
Palisade
Tightly packed, the surface
Minimal
Stomata (pl. stoma) open to release O2 and take in CO2
Cuticle (wax) protect from water loss
Root
Absorb, anchor, and store
Tissues
Pholem
Bring sugar to root
Xylem
Water and mineral to the rest of the shoot
Photosynthetic
N/A (underground)
Support
Supports holding structure of stored materials
Dermal
Control material movement
Cell Theory
All cells arise from pre-existing cells
Cells are the basic units of life
All living things are made of cells
DNA
Made from
Phosphate backbone
Hydrogen bonds between nucleotides
Nucleotides
Cytosine
Guanine
Thymine
Adenine
Makes
Chromosomes
Chromatids
Chromatin
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Unspecialised Cells
Advantages and disadvantages
Disadvantages
Always prepared for task less energy wasted preparing
Evolves faster
Focus on fewer tasks at once and do the work more efficiently
Advantages
Requires complex structure to allow for it to work
Interdependence
Stem cells
Adult
Examples
Neural stem cells
Create neurons
Bone marrow cells
Create red blood cells
Highly specialised
Pluripotent
Semilimited
Based off location in embryo
Until birth
Totipotent
Can turn into any cell
Purpose to divide
3-4 weeks start specialisation
<2 week old embryo
Cancer
Treatment
Surgery
Remove the cancerous cells
Radiation Therapy
Mutate cells so much they can't do mitosis
Chemotherapy
Chemicals target fast growing cells
Cancerous cells
Effect
Grows uncontrollably
Causes problems with organ functions
Forms tumour
Cause
Fucked up DNA fucks up division
Shitty parents (inherited DNA)
Exposure to carcinogens
Meristem cells
Cambiums
Vascular
Creates xylem and phloem
Cork
Outer layer, bark
Intercalary
Pushes out (i.e leaves)
Apical
Out from tip (i.e roots and branches)
Imaging
Endoscopy
Camera through an orfice
(Radiograph) X-ray
High energy waves passes through most
things except for bone getting an image
MRI
Big electromagnets
Can be all of them
Shitty version
CT-scan
X-Ray ring takes slices
Ultrasound
How it works
Live image
High frequency sounds
Basically echolocation
Systems serviced
Animal Systems
Muscular
All muscles
Movement
Integumentry
Skin
Protection
Immune
Lymph nodes
Fight infection
Excretory
Liver
Kidneys
Remove wastes
Endocrine
Pancreas
Pituitary gland
Chemical messages (hormones)
Reproductive
Testicles ♂
Ovaries ♀
Reproduce (the meaning of life)
Skeletal
All Bones
Support and protect
Nervous
Spinal cord
Brain
Sending electrochemical messages
Digestive
High concentration to low concentration
Fish, amphibians, and mammals
Worms and Insects
Teeth
Mechanical digestion
Spiracles
Stomach
Mechanical and chemical digestion
Intestine
Absorb
Gizzard
Crush with stones (mechanical digestion)
Crop
Store
Break down & absorb nutrients
Respiratory
Lungs -> left side of heart
Lungs (immature) + Cutaneous respiration
Gills
Countercurrent flow
Cutaneous respiration
Diffusion
Lungs
Exchange Gases
O2 in CO2 out
Circulatory
Animal Groups
Mammals
Double loop
4 chambered heart
Amphibians
Incomplete loop
3 chambered heart
Fish
2 chambered heart
Insects
Open system Haemolymph
Haemolymoph = insect blood
Worms
Single loop
5 aortic arches
Unicellular
N/A
Major Organs
Blood vessels
Capillaries
Blood from body to heart
Veins
Between arteries and capillaries, move wastes
Arteries
Blood from heart to body
Heart
Ventricle
Move blood (output)
Atrium
Collect blood (input)
Function
Move Materials