av isabella cappiello 6 år siden
465
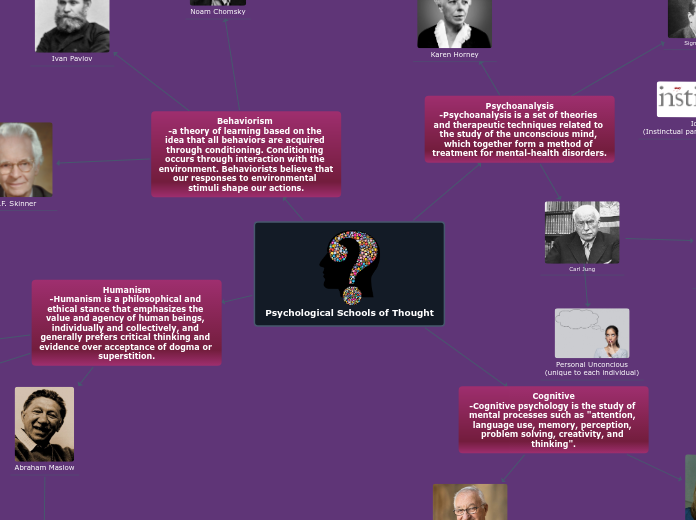
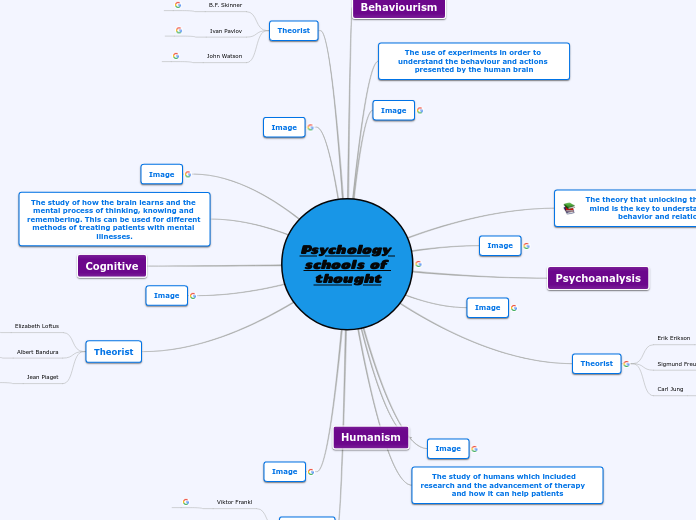
Psychological Schools of Thought
Humanism, cognitive psychology, psychoanalysis, and behaviorism are key psychological schools of thought, each offering unique perspectives on human behavior and mental processes. Humanism emphasizes the intrinsic value and potential of individuals, advocating for personal growth and fulfillment through critical thinking and evidence-based approaches.