Oxygen and carbon dioxide have to diffuse through 2 thin walls.
Tissues
(cells requiring oxygen and
and producing carbon dioxide)
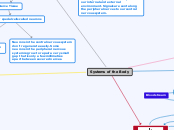
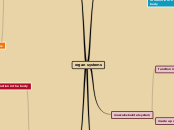
Systems of the Body
Nervous System
Sensory Receptors receive input from our internal and external environment. Signals are sent along the peripheral nerves to our central nervous system.
Found in brain, spinal cord, and nerves
Made of special cells called neurons
Neurons in the central nervous system don't regenerate easily. Some neurons in the peripheral nervous system regrow to repair a very small gap that is only a few millimetres apart between severed nerves.
Axons of limited neurons are covered by myelin.
Myelin acts like insulation on an electrical wire.
Prevents electrical impulses from passing to the wrong neuron.
Conducts electrical signals from one area of the body to another.
An estimation of 100 billion neurons in the brain
Peripheral Nervous System
(3 groups of nerves)
Regulate involuntary functions
like breathing heartbeat and digestion.
Carry info from sensory organs, like eyes ears, tastebuds, and touch receptors to the brain.
Control the voluntary muscles
Central Nervous System
Shielded by bones.
Brain and Spinal cord
Surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid.
-Cushions the brain and spinal cord from injury
-Transports chemicals and removes waste produced by the brain
Spine guards protect the spinal cord.
Skull protects the brain.
Made up of the brain, spinal cord
and peripheral nerves
Musculoskeletal System
Skeletal System
Cartilage
-Dense connective tissue mainly found in the ear, nose, esophagus, disks between vertebrae, and joints
-Made up of special cells in a matrix of collagen fibres
-Provides strong, flexible, low-friction support for bones and other tissues
-prevents damage to the ends of bones
Ligaments
-Tough, elastic, connective tissues
that hold bones together at the joints
-Made up of mostly long fibres of collagen
Bones
-Hard and dense
-Consists of bone cells within matrix of minerals (mainly Calcium and Phosphorus) and collagen fibres
-Canals inside bones have nerves + blood vessels
-Small percentage of bone tissue is living
-Stores calcium and other minerals that are needed by the organism
Muscular System
3 Types of Muscle Tissue
Muscles can pull but not push.
Cardiac Muscle
Only in the heart, another example
of a smooth muscle (involuntary)
Smooth Muscles (involuntary)
Involuntary muscles expand and
contract without a conscious thought. you aren't able to control these muscles.
Skeletal Muscle (voluntary)
Always work in opposing pairs or groups
Voluntary muscles allow you to control
them with a conscious thought.
-Consists of bundles of long cells called muscle fibres that contain specialized proteins
-Proteins cause the muscle to contract
-Contracting of the muscles causes them to get shorter and thicker
Respiratory System
Gas Exchange
Oxygen
Bloodstream
The Mouth/The Nose
The Trachea (windpipe)
Bronchi (singular: bronchus)
Alveoli (singular: alveolus)
Lungs
(air containing oxygen
carbon dioxide, and
other gases)
Circulatory System
Blood Vessels can be:
Capillaries
Are tiny blood vessels with very
thin walls that allow substances
to diffuse between blood and other
body fluids.
Veins
Carry blood toward the heart
(under lower pressure + walls
of veins aren't as thick)
Arteries
Carry blood away from the heart
(under greater pressure than
blood in other vessels)
The Heart (3 types of tissue)
Connective Tissue
Nerve Tissue
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
-Special tissue only found in the heart
-All cardiac muscles in the heart
contract at the same time
-Pumps blood around the body
Blood (4 components)
Plasma
-Protein rich liquid
-Carries blood cells through the
circulatory system
-Makes up over 50% of the
blood's volume
Platelets
-Tiny cells that help in the case of
blood clotting
-Makes up less than 1% of the
volume of blood
White Blood Cells
-Recognizes + destroys invading bacteria
-Less than 1% of the blood's volume
-Only blood cells to have a nucleus
Red Blood Cells
-Most plentiful
-Makes up about 50% of
the blood's volume
-Has a protein called hemoglobin
-Hemoglobin allows red blood cells to transport oxygen through the body
-Hemoglobin makes cells red
Digestive System
Accessory Organs
Gall Bladder
Stores bile that is created by the liver.
Pancreas
Produces insulin.
Breaks down the sugar that is consumed.
Regulates our glucose level.
Liver
Produces bile.
A liquid that breaks down fats in our food
The Mouth
The Esophagus
The Stomach
The Intestine
Small Intestine
Absorbs nutrients and minerals
from food.
Large Intestine
Absorbs water from remaining
leftover food
Between the stomach + anus.
Produces mucus.