por JONATHAN MARCELO NASIMBA TOCA 3 anos atrás
398
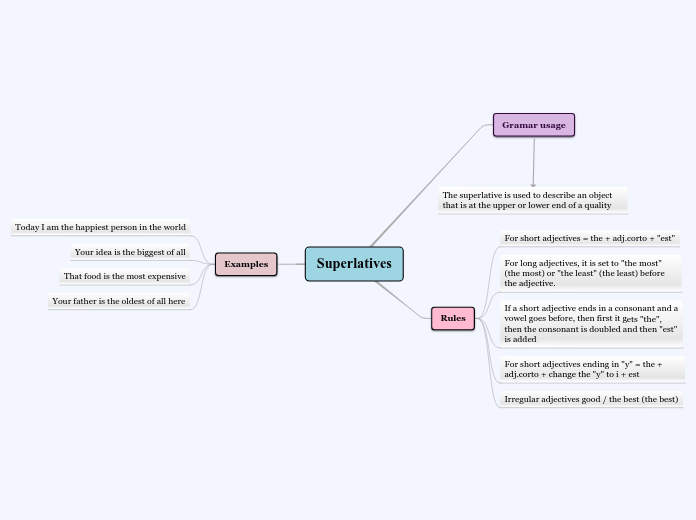
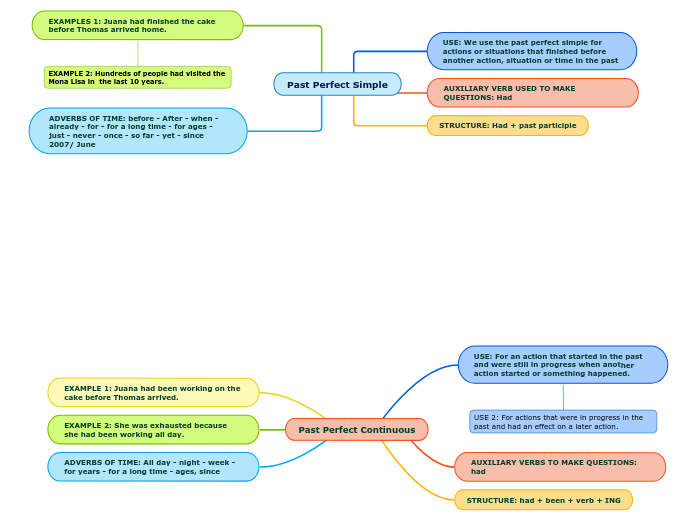
CURRICULUM, THE APPROACHES AND METHODS, AND THE NUÑEZ AND BODEGAS
Language teaching has a rich history spanning over 500 years, with early methods rooted in the teaching of Latin. The Grammar-Translation Method was prevalent, emphasizing the ability to read and understand literature through grammar rules, vocabulary lists, and translation exercises.