por Jessika Vroman 4 anos atrás
315
EDPsych: Mod 2
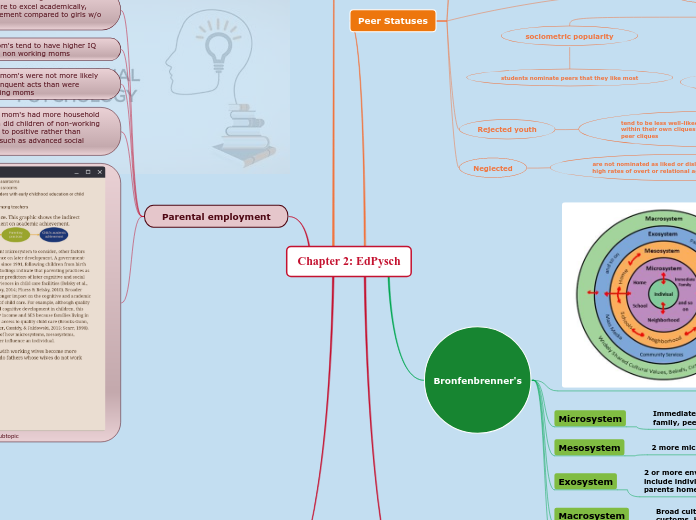
A comprehensive look at Bronfenbrenner's ecological systems theory reveals the various layers of environmental influence on human development. These include the microsystem, which encompasses immediate environments such as family and school, and the macrosystem, which involves broader cultural patterns like beliefs and morals.