por 22-0085 2 12 meses atrás
238
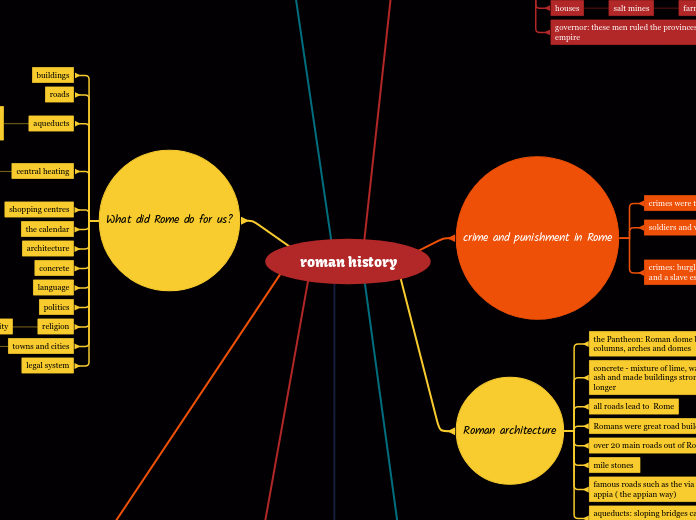
roman history
The Roman Forum served as the central marketplace and was traversed by the Via Sacra, a significant road. Roman religion included various deities like Juno, Mercury, Jupiter, Venus, Neptune, and Mars, and families maintained a shrine called a larium in their homes.