Floating topic
Experiments
Hershey and Chase
DNA Phosphorus
Settled in pellet
protein Sulfur
Found in supernatum
Subtopic
Griffiths
proved genetic material could be passed through bacteria
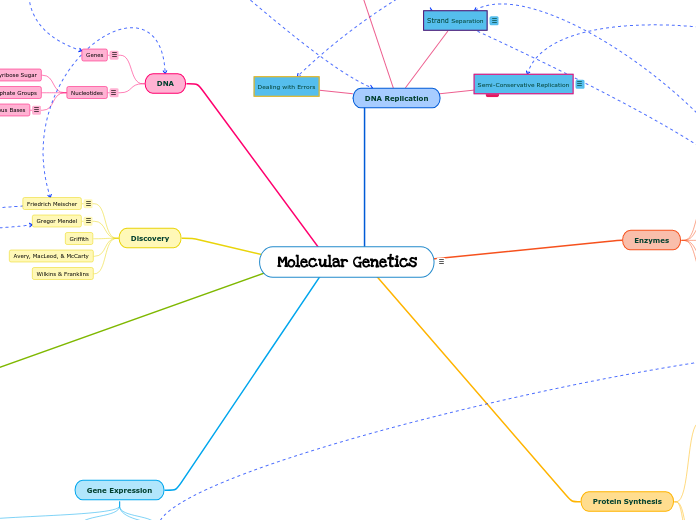
DNA Replication
unzipped by Helicase
kept apart by SSB
stress relieved by topoisomerase
replication begins at ORI
5' to 3' direction
leading strand with primase and DNA pol III
lagging strand and DNA pol I
direction of replication goes into fork and ligase seals gaps
semi conservative proved by Messleson and Stahl experiment
short GC rich sequences create mRNA foldiing
without rho factor
Promotes mRNA polymerase dissociation
requires ATP
with rho factor
Vesicle
Golgi Body
Plasma Membrane
Lysosome
Aminoacyl tRNA Synthetase
initiator tRNA scans mRNA for start codon & large subunit joins the translation initiation complex (other proteins called initiation factors may be involved)
in the ER, translation continues and the signaling peptide is cleaved by an enzyme called Signal Peptidase
no tRNA corresponds to a stop codon, so a release factor in the A site disassociates the complex and stops translating the mRNA (a GTP driven process)
in the elongation stage, a polypeptide chain begins as new amino acids are brought to the A site and attached to the previous one. the empty tRNA moves then moves to the P site after the amino acid chain was transferred
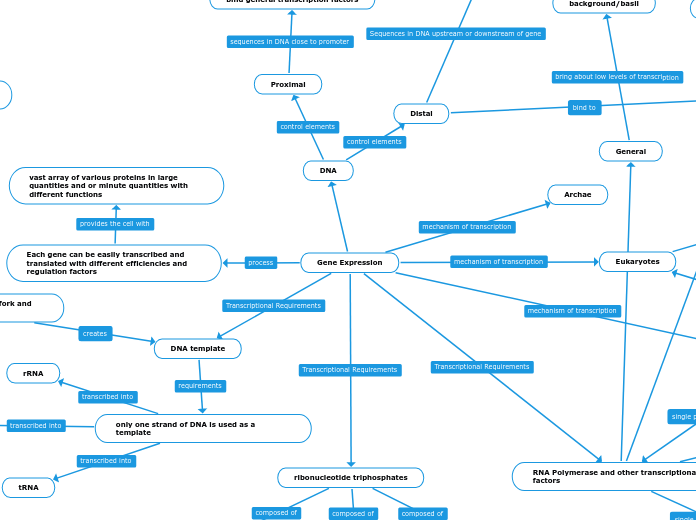
Gene Expression
Distal
Enhancers
Proximal
bind general transcription factors
Prokaryotes
Lac operon
Lactose present
repressor binds to Lactose
Glucose present
Adenylyl cyclase is inactive
cAMP levels are low
CAP is inactive
Operon is OFF
Adenylyl cyclase is active
cAMP levels High
CAP is active
Operon is ON
repressor binds to operator
Operon is OFF basil
Binding of RNA to DNA
Promoter
sigma factor of polymerase recognizes promoter region
not transcribed
recognized even in helical double stranded form
Orientation to polymerase
initiation of transcription
RNA polymerase
elongation in 5' to 3' direction
creates phosphodiester bond between NTP and sugar
protein
nucleosomes
DNA
histones
H4
H3
H2B
H2A
histone core
H1
Archae
RNA Polymerase and other transcriptional factors
Specific
changes level of transcription
Repressors
Activators
General
background/basil
three multimeric structures
RNA polymerase III synthesizes small RNA such as tRNA
RNA polymerase I synthesized rRNA
RNA polymerase II primary one
Orientation and facilitates RNA Polymerase Binding
elongation
termination
inactivated by phosphatases
site for addition of poly A tail
poly A tail
methylation
capping
ribonucleotide triphosphates
phosphate group
ribose sugar
sugar phosphate backbone
encodes
Nitrogenous base pair
Pyrimides
Single-ring structure
CTP
purines
GTP
ATP
UTP
Double-ringed structure
DNA template
only one strand of DNA is used as a template
mRNA
Translation/Protein Movement
Proteins in the Endomembrane System
Nucleus
Chloroplasts
Peroxisomes
Mitochondria
Secretory Pathway
Polypeptide synthesis on a free ribosome
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Cytoplasm
Steps in Translation
Prokaryotic
Elongation
Termination
Eukaryotic
Initiation
Ribosomes
Large and Small subunits
codons
tRNA
Binding Sites
E site
P Site
Peptidyl Transferase
A Site
Amino Acids
anticodons
transcription
occurs downstream from +1
promoter found upstream
Eukaryotes
transcription in nucleus
RNA pol II
pre-mRNA
RNA splicing
introns are spliced out
exons remain in final mRNA
5' end cap and 3' poly A tail
prokaryotes
transcription in cytoplasm
RNA pol
Transcetylase
Permease
Beta Galactosidase
rRNA
Each gene can be easily transcribed and translated with different efficiencies and regulation factors
vast array of various proteins in large quantities and or minute quantities with different functions