References
Met, M. (1999, January). Content-Based Instruction: A Relevant Approach of Language Teaching. Washington, DC: The National Foreign Language Center. Dialnet-ContentBasedInstruction-5181354.pdf.
Brown, H., & Bradford, A. (2017). EMI, CLIL, & CBI: Differing approaches and goals. In P. Clements, A. Krause, & H. Brown (Eds.), Transformation in language education. Tokyo: JALT.
Master’s program on learning and teaching processes in second languages, Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana.
Third semester – English Emphasis III
Student: Sonia Viviana González Castro
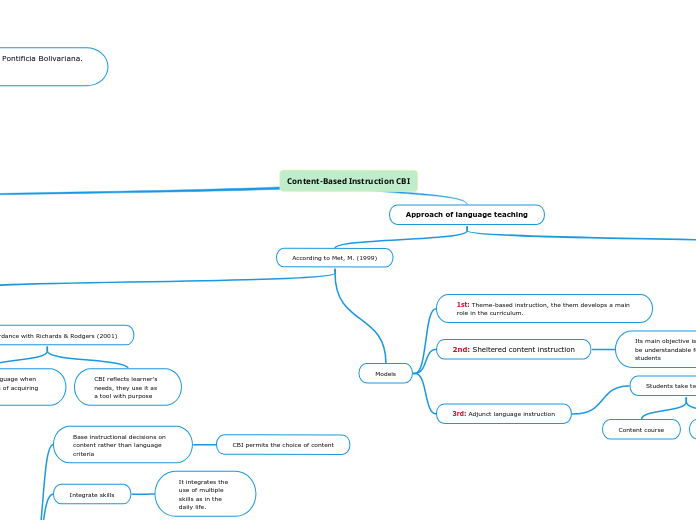
Content-Based Instruction CBI
Approach of language teaching
Drawbacks
The fundamentals of other approaches that would enrich the practice are not taken into account
Due to its characteristics, it prioritizes the content and part of the grammatical structure is addressed not in a particular way, but in a general way.
According to Met, M. (1999)
Models
3rd: Adjunct language instruction
Students take two courses
Lingustic course
Content course
2nd: Sheltered content instruction
Its main objective is to be understandable for students
1st: Theme-based instruction, the them develops a main role in the curriculum.
Basic principles
As specified by Brinton (2003)
The resources are authentic
It promotes the use of real life examples
Content takes importance for its relevance and interest to the students.
Students participate actively
It is learner-centered, not teacher-centered
Integrate skills
It integrates the use of multiple skills as in the daily life.
Base instructional decisions on content rather than language criteria
CBI permits the choice of content
In accordance with Richards & Rodgers (2001)
CBI reflects learner's needs, they use it as a tool with purpose
People learn a 2nd language when they use it as a means of acquiring information.
According to Brown, H., & Bradford, A. (2017) it could be defined as:
“the use of English to teach academic subjects in countries or jurisdictions where the first language (L1) of the majority of the population is not English” (Dearden, 2015, p. 4)
“English-taught degree programs . .. predominately aim at the acquisition of subject knowledge” (Unterberger, 2014, p. 37).
“an umbrella term for academic subjects taught through English, one making no direct reference to the aim of improving students’ English” (Dearden & Macaro, 2016, p. 456)
“focuses on content learning only” (Smit & Dafouz, 2012, p. 4)
“The central focus is on students’ content mastery and no language aims are specified (Unterberger & Wilhelmer, 2011, p. 96)
Subtopic