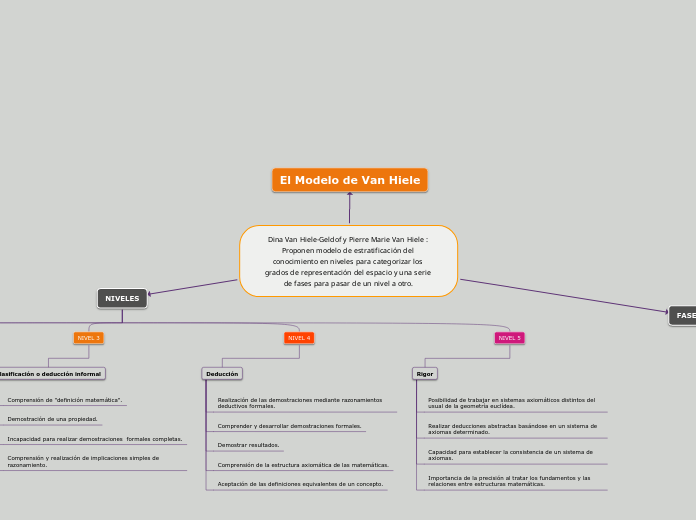
Dina Van Hiele-Geldof y Pierre Marie Van Hiele : Proponen modelo de estratificación del conocimiento en niveles para categorizar los grados de representación del espacio y una serie de fases para pasar de un nivel a otro.
Name the character
Type in the name of the character whose change throughout the story you are going to analyze.
Example: Nick Carraway.
FASES
Character's behavior
Think of the character's behavior at the beginning of the story and look for the way it changed throughout the story.
FASE 5
Intregración
FASE 4
Orientación libre
FASE 3
Explicación
The reason for the change in behavior
What caused the character to change the first behavior you mentioned? Type in the reason for the change.
Example: 'because no one else was interested ', and he felt Gatsby shouldn't be left alone in his last moments.
FASE 2
Orientación dirigida
Change in behavior
In what way did the character change the other behavior(s) you mentioned? Type in a relevant quote.
Example:
'You said a bad driver was only safe until she met another bad driver? Well, I met another bad driver, didn't I? [...]
I thought you were rather an honest, straightforward person. I thought it was your secret pride.'
FASE 1
Discrecimiento o información
Initial behavior
What is the character's behavior at the beginning of the story? Type in a relevant quote for your statement.
Example: Nick seems to be an honest person, calling himself 'one of the few honest people that I have ever known'.
NIVELES
Character's feelings
Focus on the way the character's feelings are presented at the beginning and at the end of the story, while explaining why they have changed.
NIVEL 5
Rigor
Importancia de la precisión al tratar los fundamentos y las relaciones entre estructuras matemáticas.
Capacidad para establecer la consistencia de un sistema de axiomas.
Realizar deducciones abstractas basándose en un sistema de axiomas determinado.
Posibilidad de trabajar en sistemas axiomáticos distintos del usual de la geometría euclídea.
NIVEL 4
Deducción
Aceptación de las definiciones equivalentes de un concepto.
Comprensión de la estructura axiomática de las matemáticas.
Demostrar resultados.
Comprender y desarrollar demostraciones formales.
Realización de las demostraciones mediante razonamientos deductivos formales.
NIVEL 3
Clasificación o deducción informal
The reason for the change of feelings
What caused the character to change the first belief you mentioned? Type in the reason for the change.
Example: disgust towards the lack of morality in the Buchanan family.
Comprensión y realización de implicaciones simples de razonamiento.
Incapacidad para realizar demostraciones formales completas.
Demostración de una propiedad.
Comprensión de "definición matemática".
AFTER
Análisis
Change of feelings
In what way did the character change the feeling you mentioned?
Type in a quote to support your statement.
Example: 'They are a rotten crowd. You're worth the whole damn bunch put together.' - Nick criticizing the Buchanans.
No se relacionan diferentes propiedades de una figura.
Demostración de una propiedad mediante la comprobación.
Deducción de propiedades de una figura.
Definición de un concepto.
Reconocimiento de que las figuras geométricas.
NIVEL 1
Reconocimiento o visualización
Initial feelings
How does the character feel about a certain subject at the beginning of the story? Type in a relevant quote to support your statement.
Example: "Reserving judgements is a matter of infinite hope."
No suele reconocer las partes de la figura.
Uso de propiedades imprecisas.
Aprendizaje de in vocabulario.
Percepción individual de la figura.
Figuras como un todo global.
El Modelo de Van Hiele
Title
Type in the title and author of the literary work that introduces the character.
Example: The Great Gatsby, by F. Scott Fitzgerald.